Review
Before discussing the characteristics of openSUSE that apply to both its regular releases, Leap -- currently at version 42.2, and its rolling release, Tumbleweed, I'll discuss Tumbleweed specifically, and how it differs from Leap (I imagine this is what most readers of this article are interested in).
In the early days of the present incarnation of Tumbleweed -- after the merge with Factory -- it shared the same artwork and theme of the openSUSE regular release, at that time 13.2. When Leap came into existence, it had its own new artwork in the form of a logo, a GRUB theme, a Plymouth theme, and a desktop background, while Tumbleweed was stuck with openSUSE 13.1 artwork and no logo. In recent months however, Tumbleweed has been getting the attention it deserves in this area with its own set of artwork and its own logo.
-
The Tumbleweed Default KDE Plasma 5.
Notice that as in openSUSE 13.2 the desktop background seems to be a stylization of geckos scales.
-
The openSUSE Tumbleweed GNOME Default Desktop
The GNOME edition uses the same background as Plasma and Cinnamon.
-
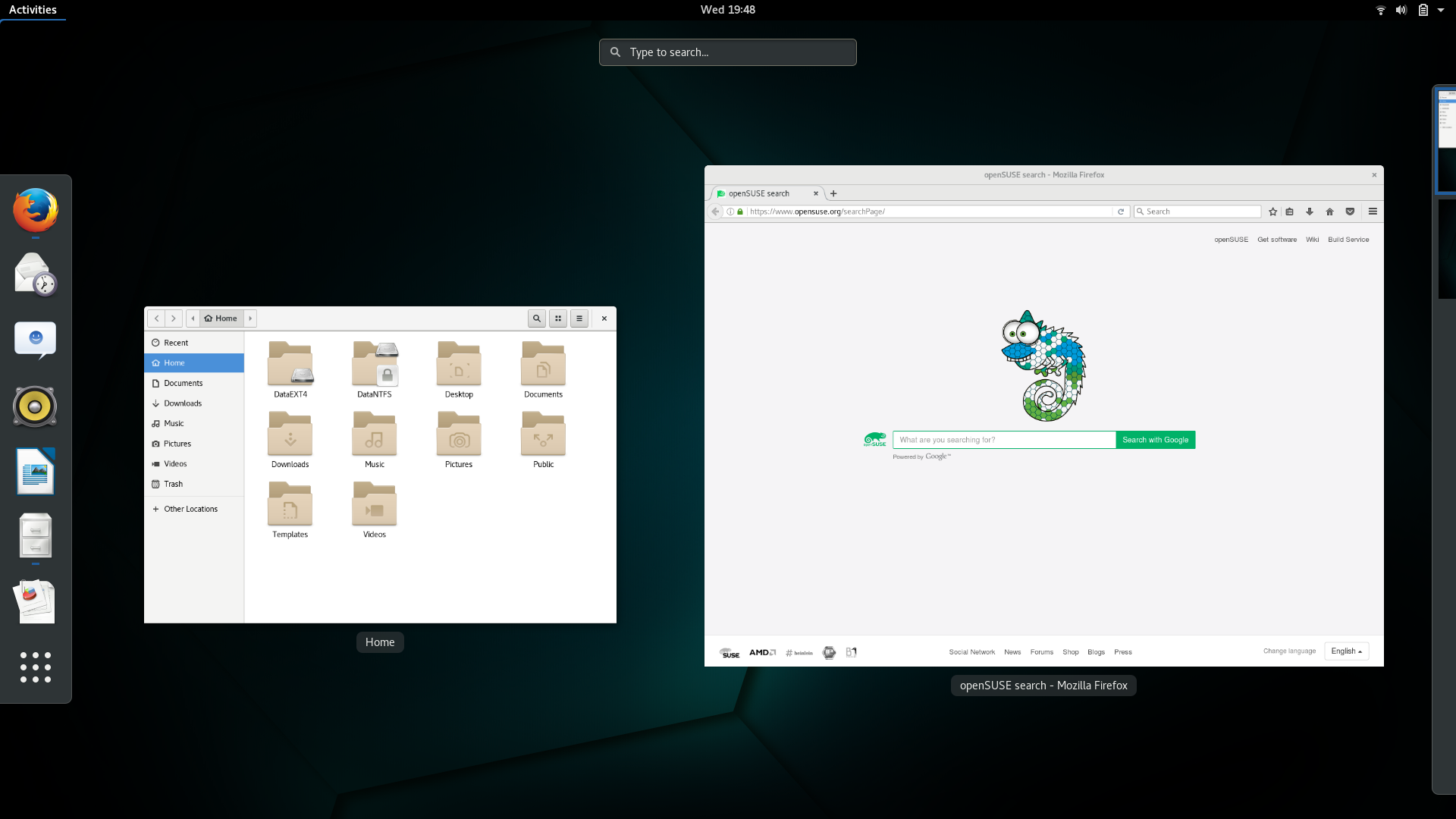
The openSUSE Tumbleweed GNOME Default Theme
Note the custom Firefox start page which includes an animated openSUSE gecko mascot. The search box incorporates an additional search engine which searches
the openSUSE Software Portal.
-
The Tumbleweed GNOME Default Theme
-

The Tumbleweed GNOME Default Theme
-
The Tumbleweed GNOME Default Theme
-
The Tumbleweed GNOME Default Theme
openSUSE Tumbleweed Artwork and Default Themes.
After months of using 13.2 or Leap 42.1 artwork Tumbleweed finally got its own artwork.
So now Tumbleweed has its own look, distinguishing it from Leap, but it has always been distinguished by a different purpose from that of Leap in that it seeks to improves the experience of desktop/laptop casual users, enterprise users, and less casual users, such as developers, who want the latest software. If you've read my reviews of 13.1 and Leap 42.1, the single most important issue I had with openSUSE was that software became outdated before the next regular release -- although optional repositories could be used to update some software. Tumbleweed also seemed to carry more software in its default repositories than Leap, at least around the time Leap 42.1 was released. In my review of Leap 42.1, I found that a very common and important program like Filezilla was not included in the default Leap repositories but was available in Tumbleweed's default repositories. Fortunately for Leap users, this seems to not be the case anymore, but the version available for Leap is much older -- as of 1 Feb 2017 filezilla-3.24.0-1.1.x86_64.rpm is available in the basic OSS repository for Tumbleweed, but only filezilla-3.12.0.2-1.1.x86_64.rpm is available in the equivalent Leap 42.2 repository (there is no Filezilla package in the Leap 42.2 updates repository).
As another example of the freshness of Tumbleweed software, openSUSE Tumbleweed made KDE's Plasma Desktop 5.9 (5.9.0), which added many new features, available in its January 31 2017 snapshot -- on the same day KDE announced the release of this version of the Plasma desktop, which was also the same day Arch made Plasma 5.9.0 available. Arch, however, was quicker in updating to the next minor version -- 5.9.1, a bugfix release -- adding it to its repositories on February 7, 2017, again on the same day KDE released it.
Tumbleweed completely solves the problem of outdated software through the rolling release model, but not at the expense of stability or by creating a high risk of breakage after updates. The only cost, as others view it, to openSUSE's model of providing timely software might be a large download when there is a large number of updated packages. Some on the internet see the snapshot method of rolling updates, where all packages are built together even when some of the actual software doesn't have an update, results in an excessive number of packages to download. On my recently retired Lenovo V570, which had eight distributions installed, so I didn't use a particular distribution regularly, there might have been an occasional update with over a thousand packages to update. Despite the complaints this isn't unusual in other rolling release distributions either. Recently, on the new Acer V 15 Nitro where I am using openSUSE almost exclusively, there may only be at most about two hundred updated packages per week and sometimes none.
Always having current software in Tumbleweed but without a loss in stability may be due to SUSE's openQA automated testing tool and the building of all packages at once together, and releasing updates as snapshots. According to the openSUSE Tumbleweed Portal:
The Tumbleweed distribution is a pure rolling release version of openSUSE containing the latest stable versions of all software instead of relying on rigid periodic release cycles. The project does this for users that want the newest stable software.
Tumbleweed is based on Factory, openSUSE's main development codebase. Tumbleweed is updated once Factory's bleeding edge software has been integrated, stabilized and tested. Tumbleweed contains the latest stable applications and is ready and reliable for daily use.
It is indeed reliable for daily use despite the warning on the openSUSE Tumbleweed Portal regarding proprietary kernel modules:
Due to the fast pace of kernel upgrade on Tumbleweed, 3rd party kernel driver modules may not be fast enough to catch up with the latest kernel version. In the unlikely case that your kernel driver module does not work on Tumbleweed, please consider using openSUSE Leap instead.
Please remember to also re-compile and re-install these third party drivers with every kernel upgrade on Tumbleweed; this includes the proprietary graphics drivers.
NVIDIA proprietary driver generally works very well with Tumbleweed.
and other warnings and dauntingly complicated instructions on other pages of the openSUSE wiki concerning Nvidia drivers. This was the reason that I had initially used the second slot on the SSD for Manjaro, thinking that it would more reliably and conveniently handle the updates of the Nvidia/hybrid graphics. But then I discovered the
openSUSE Build Service Bumblebee repository for Tumbleweed which contains packages to automate and simplify the building, installation, and update of the necessary kernel modules for the proprietary Nvidia driver for use with Bumblebee -- which I discuss in
openSUSE Tumbleweed (Snapshot 20161204) Nvidia Hybrid Graphics -- without having to use Nvidia's installer, which needs to be run after each kernel update. I was impressed with how simple the configuration of the Nvidia/Intel hybrid graphics was compared to Ubuntu, and that the simple setup had better graphics performance than both Ubuntu and Manjaro in that the framerates when using the Nvidia processor were the same as with the Intel graphics processor, unlike in openSUSE where, according to
glxgears, the framerates were ~40 times higher.
I was also pleasantly surprised by how well openSUSE Tumbleweed worked as a platform for web development -- for using the nodejs system in particular, a very important tool for web developers. The latest versions of the relevant packages are available in Tumbleweed which is not the case with Leap. And unlike with Ubuntu everything was available without having to resort to external sources, and unlike with Manjaro some ancillary components did not have to be installed separately.
-
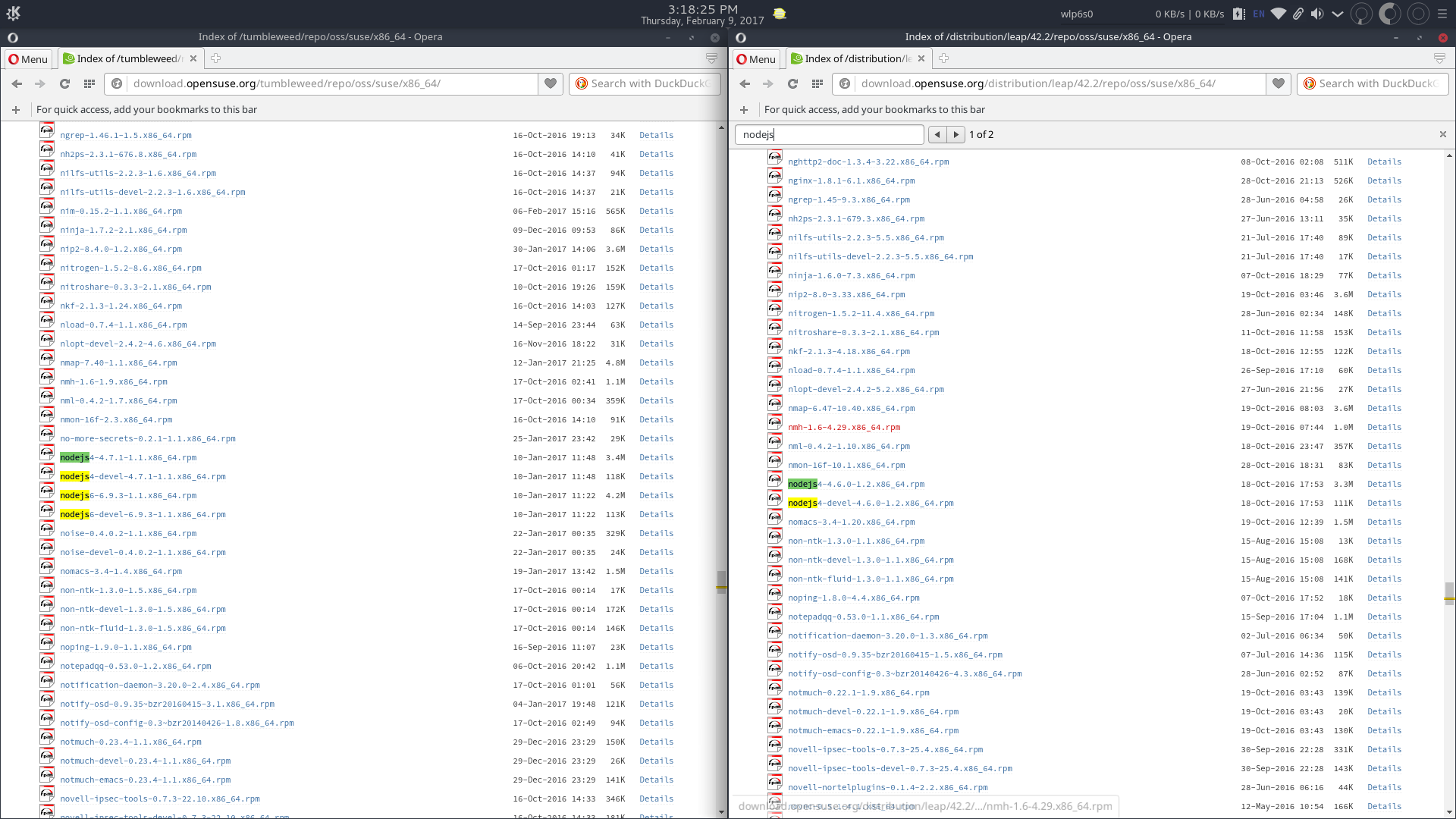
A comparison of the default OSS repositories of Leap 42.1 and Tumbleweed.
The latest production use version of nodejs (nodejs6) is available in openSUSE Tumbleweed repositories as well as an older more stable version (nodejs4).
-
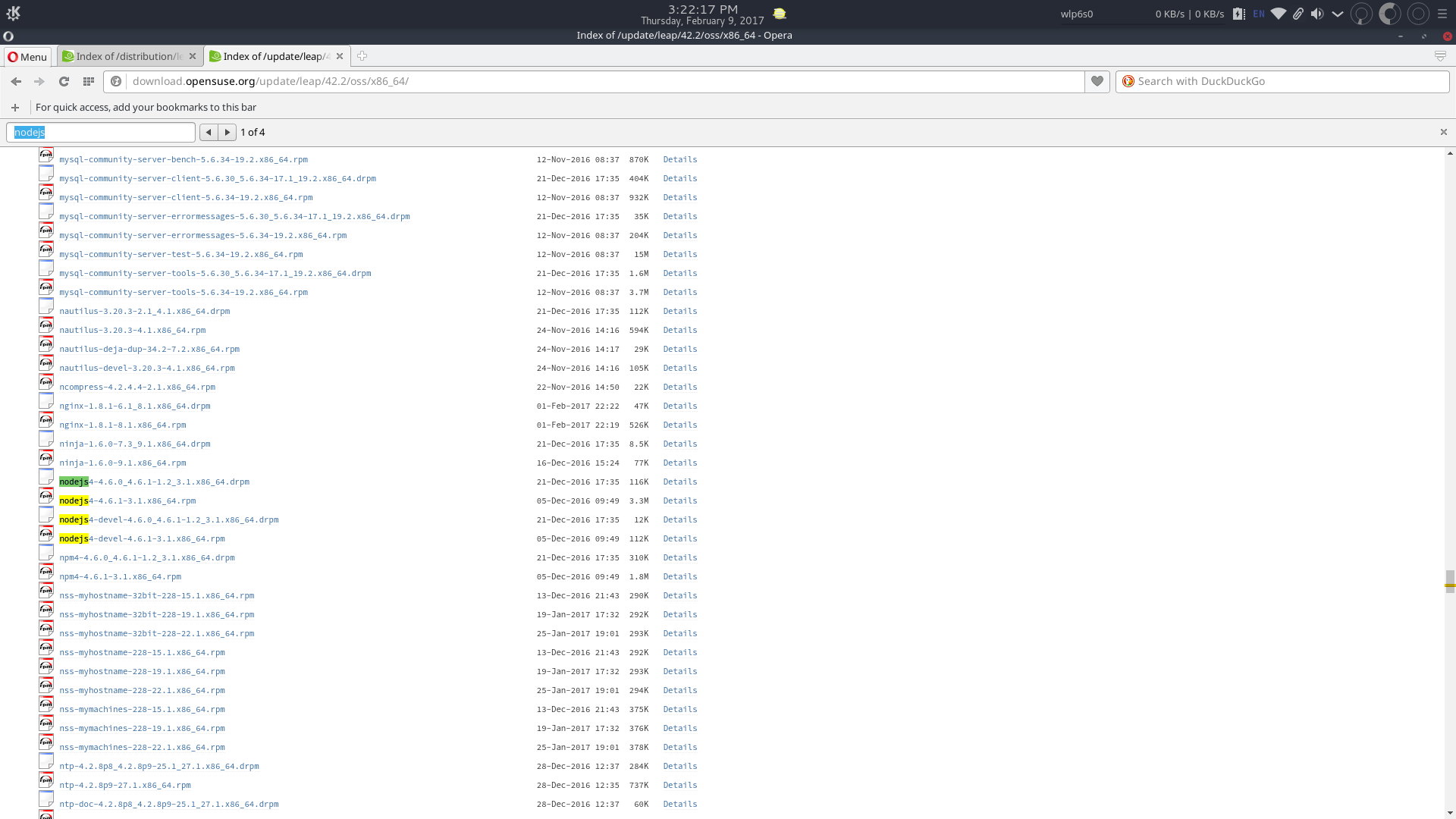
The Leap 42.2 Update repository.
Only nodejs4 is available in the Leap repository, although it has been recently updated to a new minor version.
-
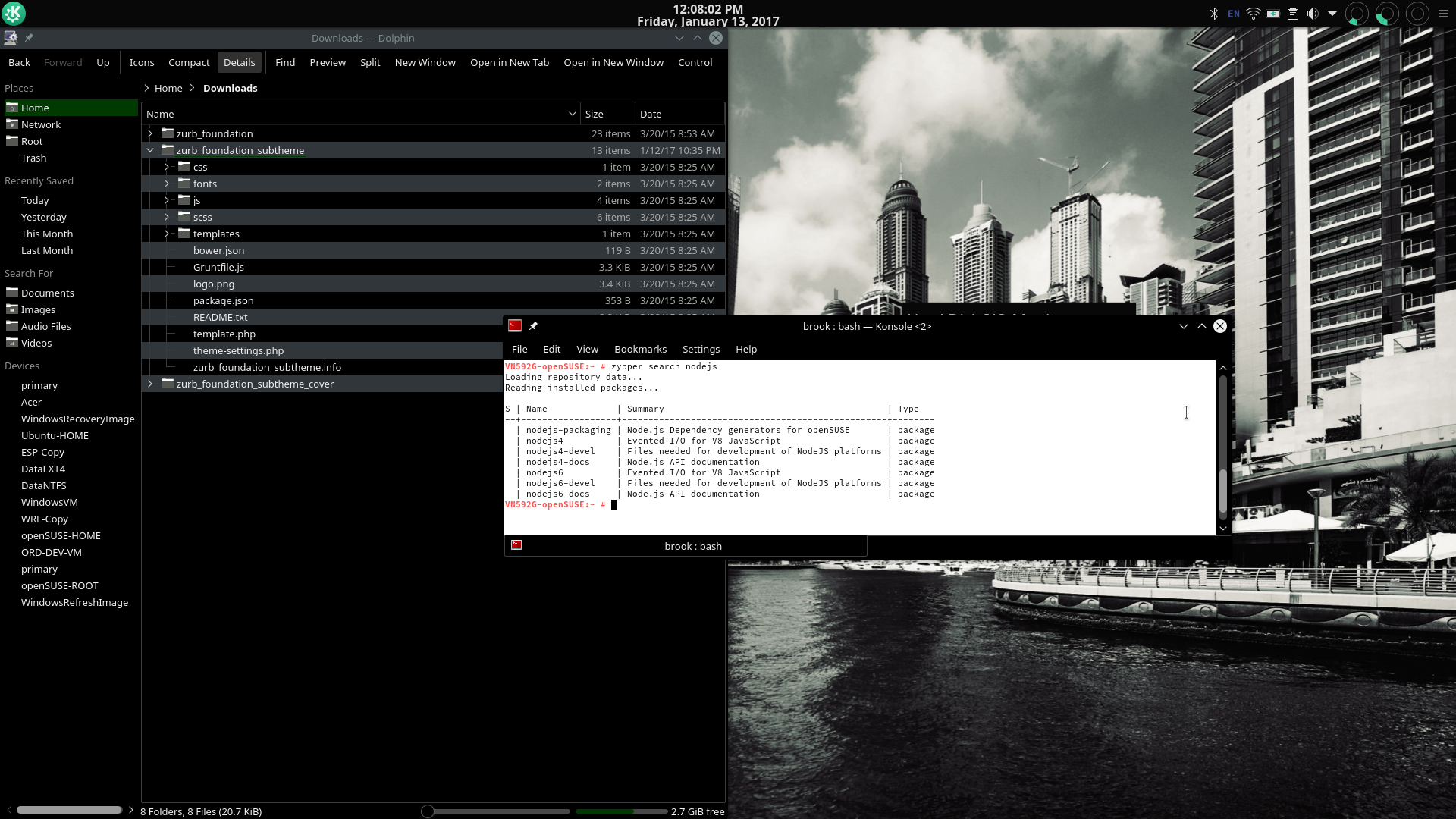
A zypper search for nodejs
The latest production use version of nodejs is available in openSUSE repositories as well as an older more stable version.
The latest production use version of nodejs is available in openSUSE repositories as well as an older more stable version.
An example of of the advantage of Tumbleweed: nodejs6 is available directly from the openSUSE Tumbleweed repositories. Compare to Ubuntu 16.04 and openSUSE leap where only nodejs4 is available from default repositories.
Tumbleweed specifically solves the problem of outdated software in Leap for users who want or need the latest software, but besides the very latest in software all the time, everything about Tumbleweed is the same as Leap -- the fundamental strengths of openSUSE generally apply to Tumbleweed. It has the same holistic design, where all of the tools work together, whether GUI or command line, and the parts don't seem to be disparate parts randomly put together; it also has the same rational design, administration power, and flexibility as the regular release openSUSE. These strengths are evident when considering its comprehensive system configuration utility suite of programs called YaST, available in GUI and command line forms, its zypper command line package and repository manager program and its configuration files, and that although it offers the GUI and command line forms of YaST components, it also allows the user to administer the system through the traditional method of editing configuration files.
The YaST suite of system configuration programs is openSUSE's most important distinguishing feature. Aside from Mandriva and its descendants' Control Center, which is much, much less feature complete, to my knowledge no other Linux distribution has anything like it. I would even dare to say that YaST makes a computer with adequate system resources running openSUSE -- in terms of subjective feel -- somewhat of a successor to the professional and polished UNIX workstations of the late 90s made by Silicon Graphics (and not Apple, ironically, which uses a UNIX core).
The Main Screen of the YaST GUI.
The YaST suite of system administration programs is unique among Linux distributions. It allows users to configure every aspect of the openSUSE system, even remotely. The openSUSE installer is actually part of the YaST system and includes some of the modules. The modules included in a default installation are not
the complete set of available YaST modules.
YaST begins to impress at installation because the installer is part of the YaST system. Many of the components of YaST in the installed system are available in the installer, such as the YaST Partitioner. It is evident that the YaST installer and the installed YaST suite are aimed at enterprise system administration. This may be undesirable for some potential users who want the absolute in simplicity, but for users who want a fine tuned installation where many options are configured during installation while using a GUI installer -- for example, data partitions that should be included in /etc/fstab with all fstab options set and not after, who have an interest in learning more about Linux, or appreciate computer user power, YaST is a great installer. Even users who may want simplicity may appreciate the other major aspect of the system that can be preconfigured during installation -- the software that should be on the system, including multiple desktop environments. The YaST installer allows users to select every bit of software that should be included in the installed system, either from the 4.7 GB install media or if the network is configured from the normal repositories. (See the slides of the installation on the next page).
YaST curses Mode Running in Konsole.
The YaST suite can also be run in interactive mode in a terminal, a mode useful for administering a system remotely. Unfortunately the keyboard controls indicated by the program except the Fn keys didn't work in my installation of Tumbleweed.
After installation the YaST module that will be used by most people who prefer GUI programs for package management will be the Software Management module. A close second may be the Software Repositories module. Since these are discussed in some other pages on the site (review of 13.1, review of Leap 42.1, and introduction to openSUSE repository management), I'll mention some others that are useful but may only be used rarely. In all cases these GUI tools greatly simplify some system administration tasks and do so in a way that is not possible in other distributions.
One such module is the Sudo module, which allows the configuration of sudo. This module does not simply add a user to the sudo group, but allows the same configuration of sudo as can be done manually by using visudo to edit the configuration file /etc/sudoers as mentioned in the Arch Wiki page on the configuration of sudo.. The slides below show some of the screens of the Sudo module.
-
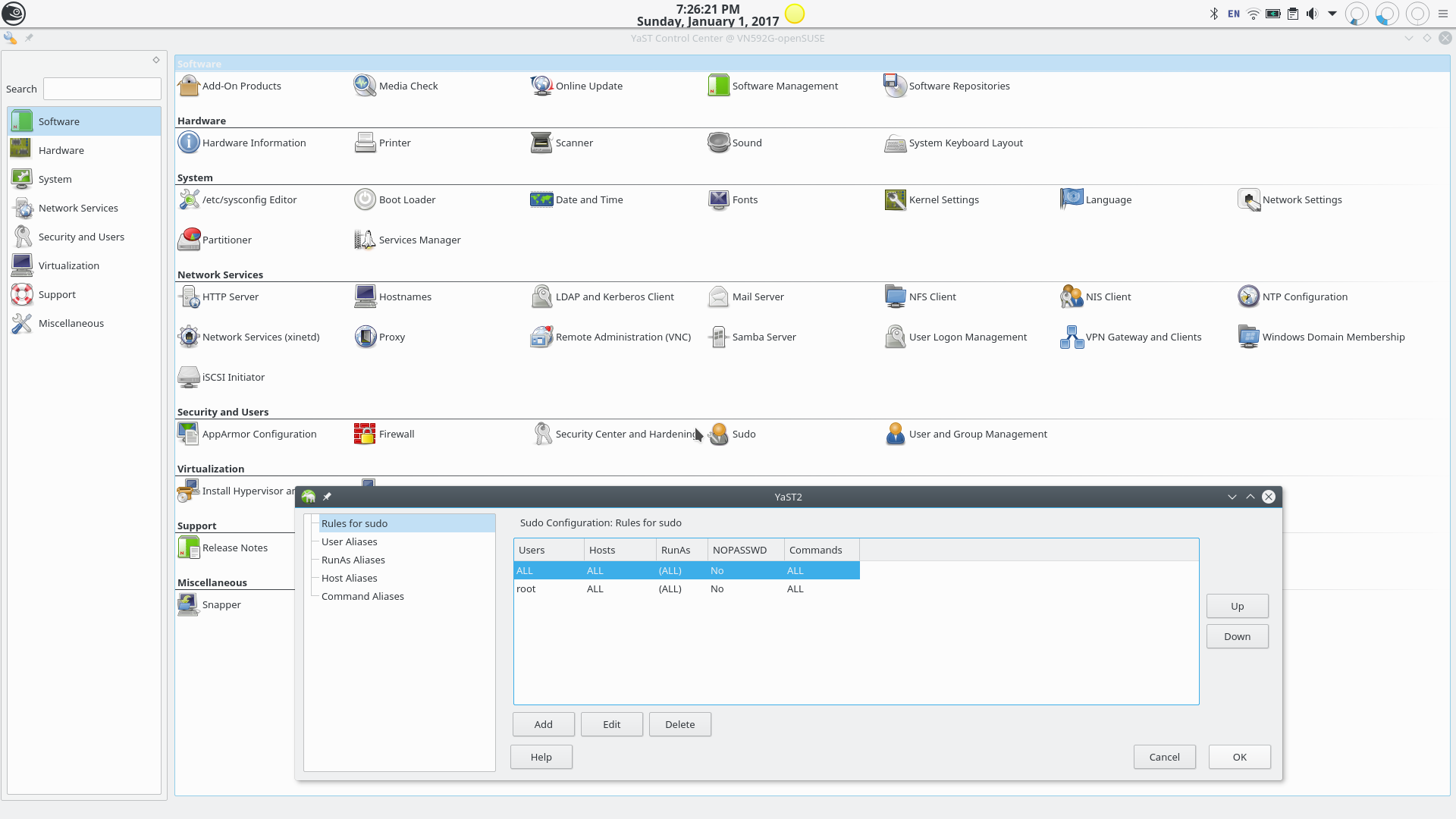
The Rules for Sudo Section of the YaST sudo Module.
Note how the structure of what is found in the /etc/sudoers configuration file is reproduced here.
-
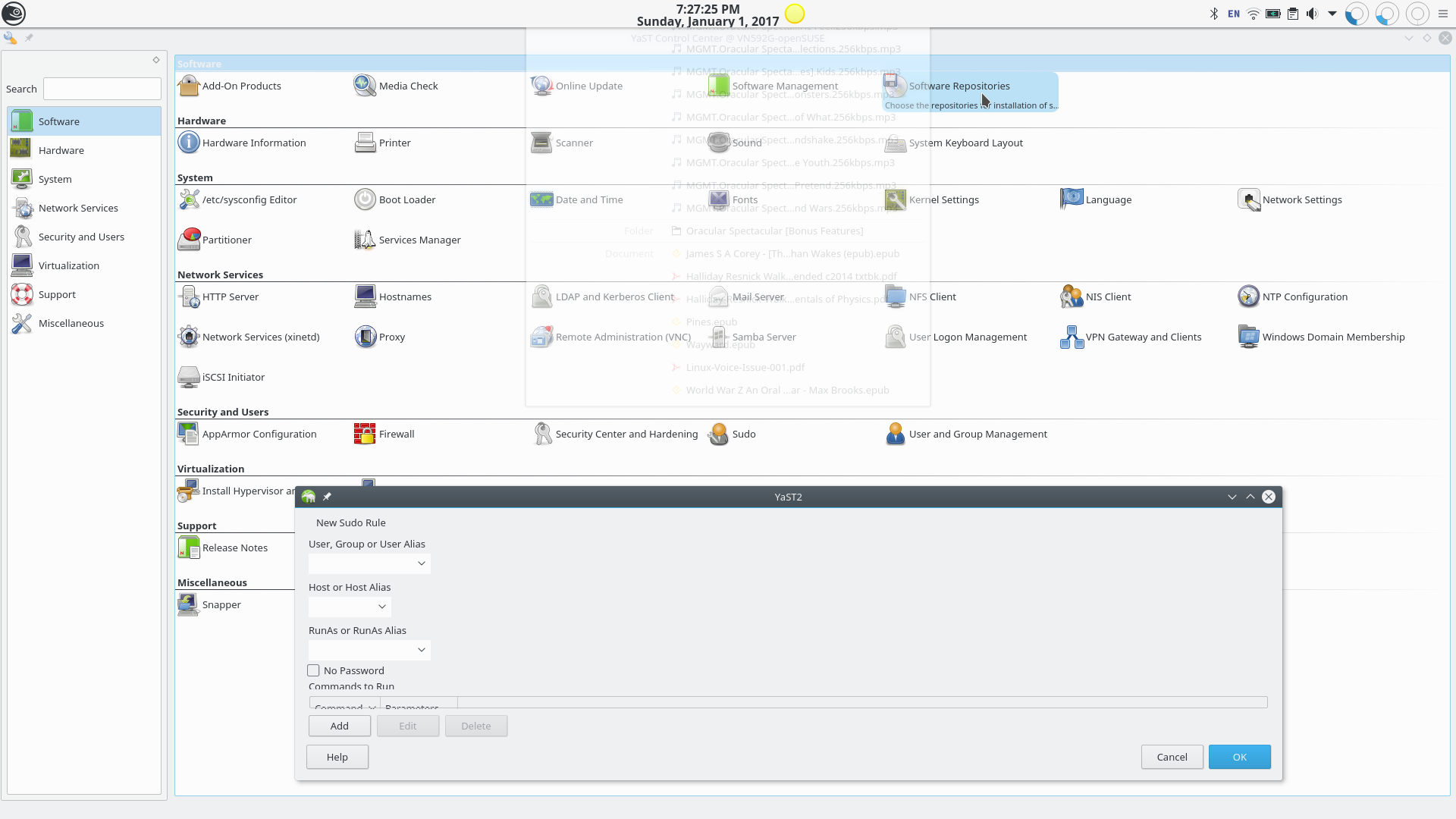
Adding a New sudo Rule.
Adding a rule here will add a rule to the /etc/sudoers configuration file.
-
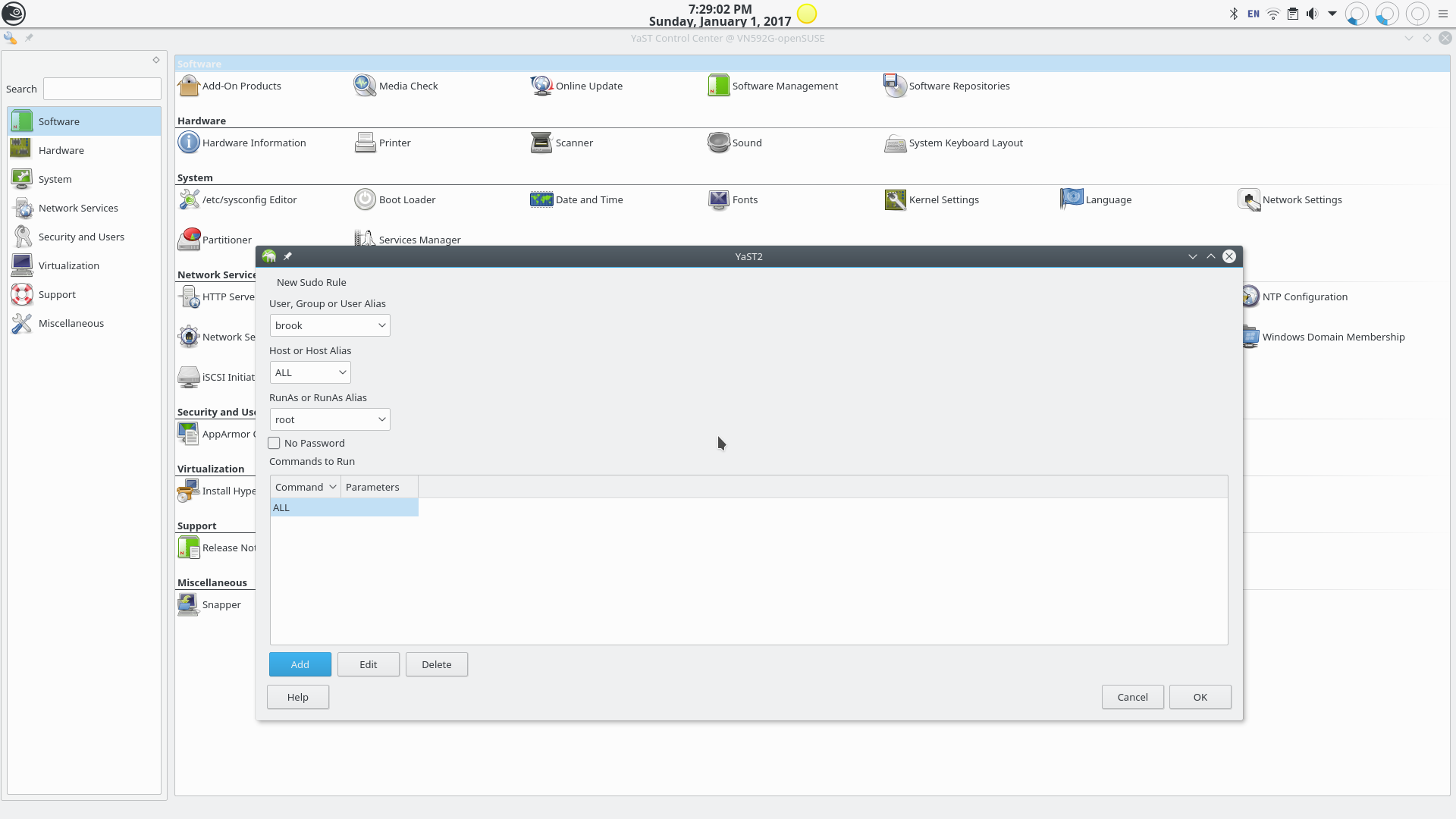
Adding a New sudo Rule.
Adding a rule here will add a rule to the /etc/sudoers configuration file.
The YaST Sudo Module.
The YaST sudo module, as the name implies, allows system administrators to manage sudo. In this series of slides I am enabling sudo privileges for my user (brook).
Some of the other modules in the YaST suite include a module for managing users and groups, a module for managing systemd services, a module for modifying kernel settings, and a module for configuring the bootloader.
-
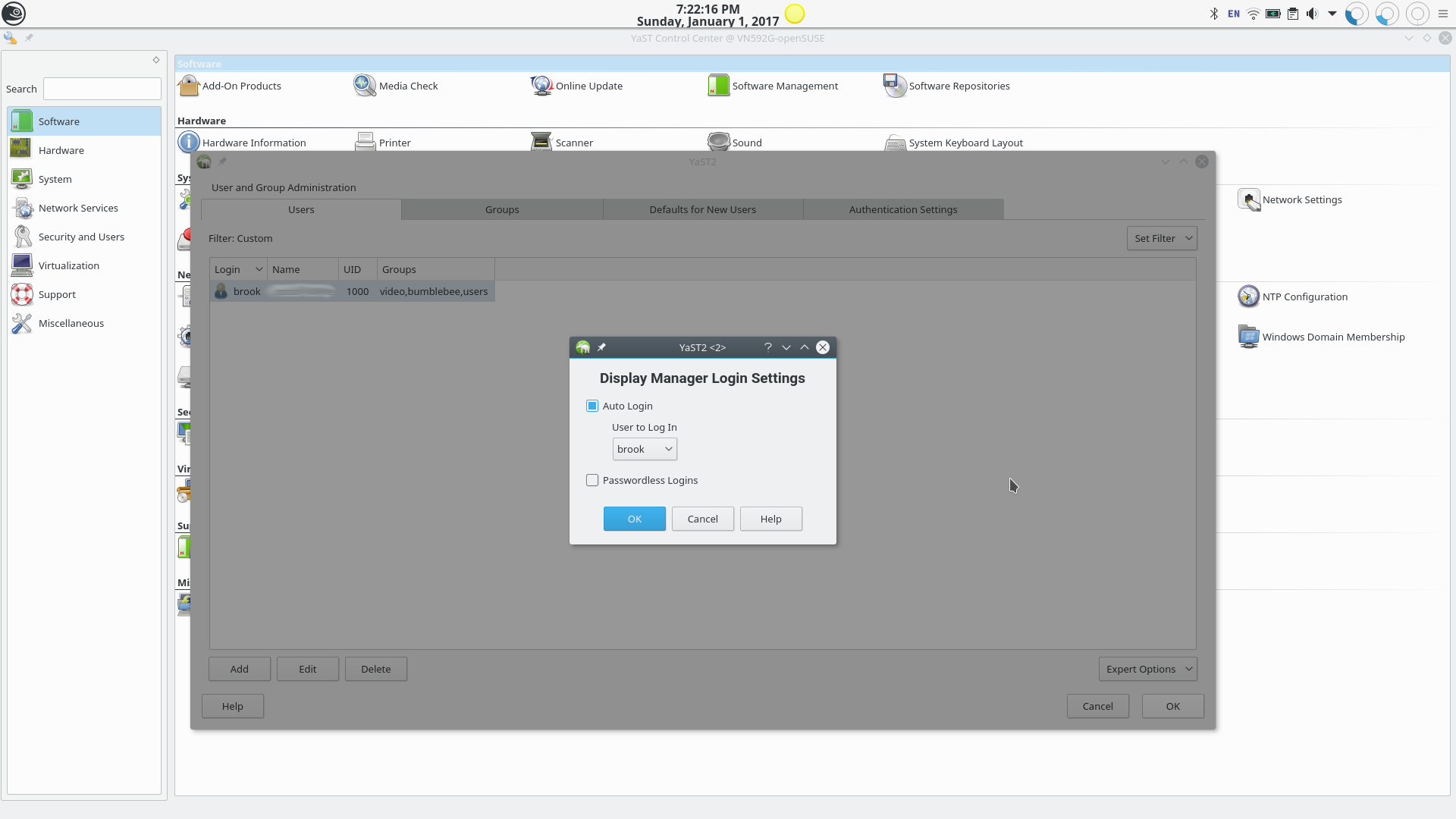
YaST Users and Groups Module
Managing auto login in the YaST Users and Groups module.
-
YaST Users and Groups Module
The Groups section of the module.
-
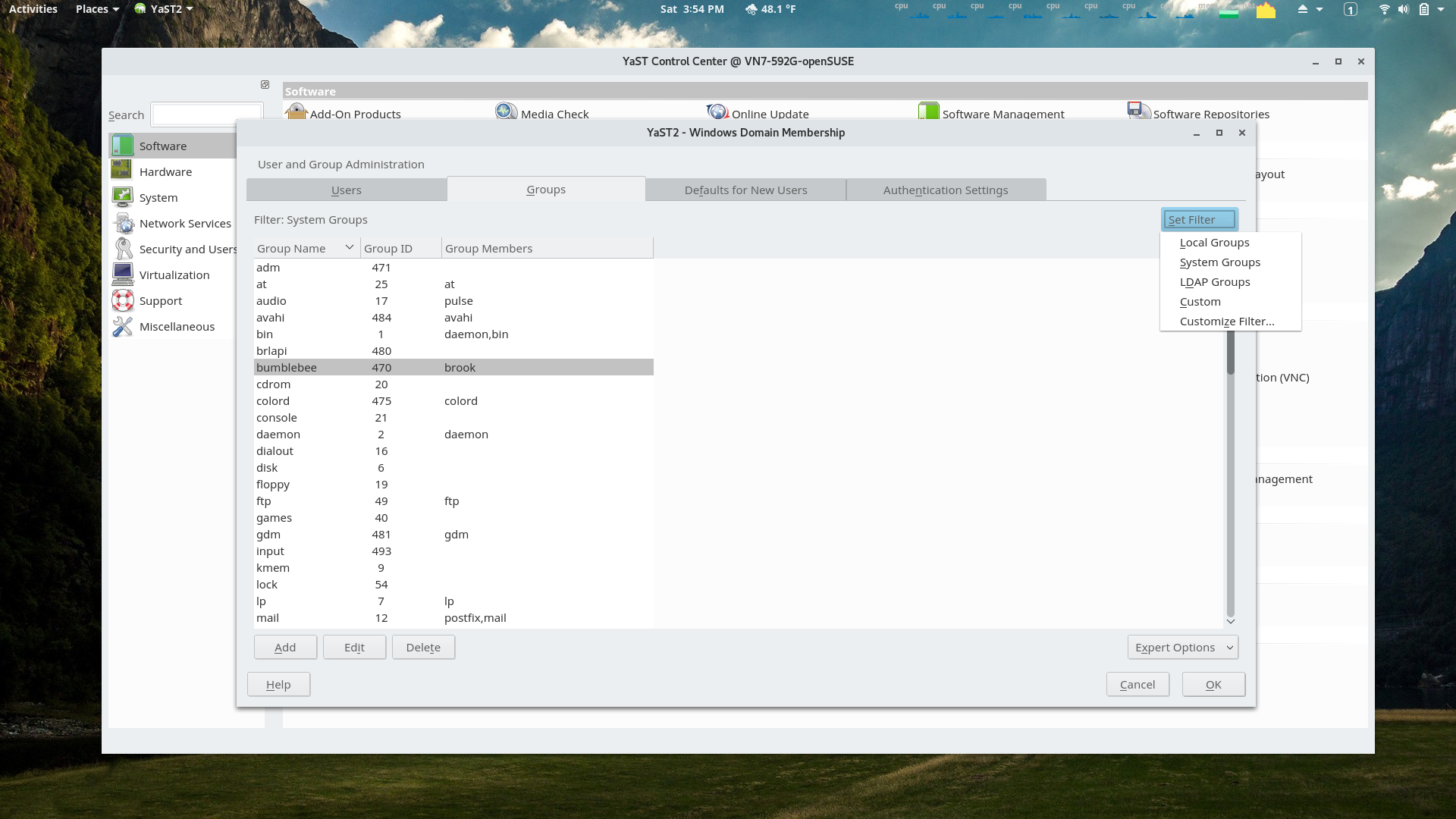
YaST Users and Groups Module
Displayed users and groups can be filtered by type. Note that my user is in the bumblebee group added by command line as discussed in the Nvidia Hybrid Graphics article but could have been added using this YaST module.
-
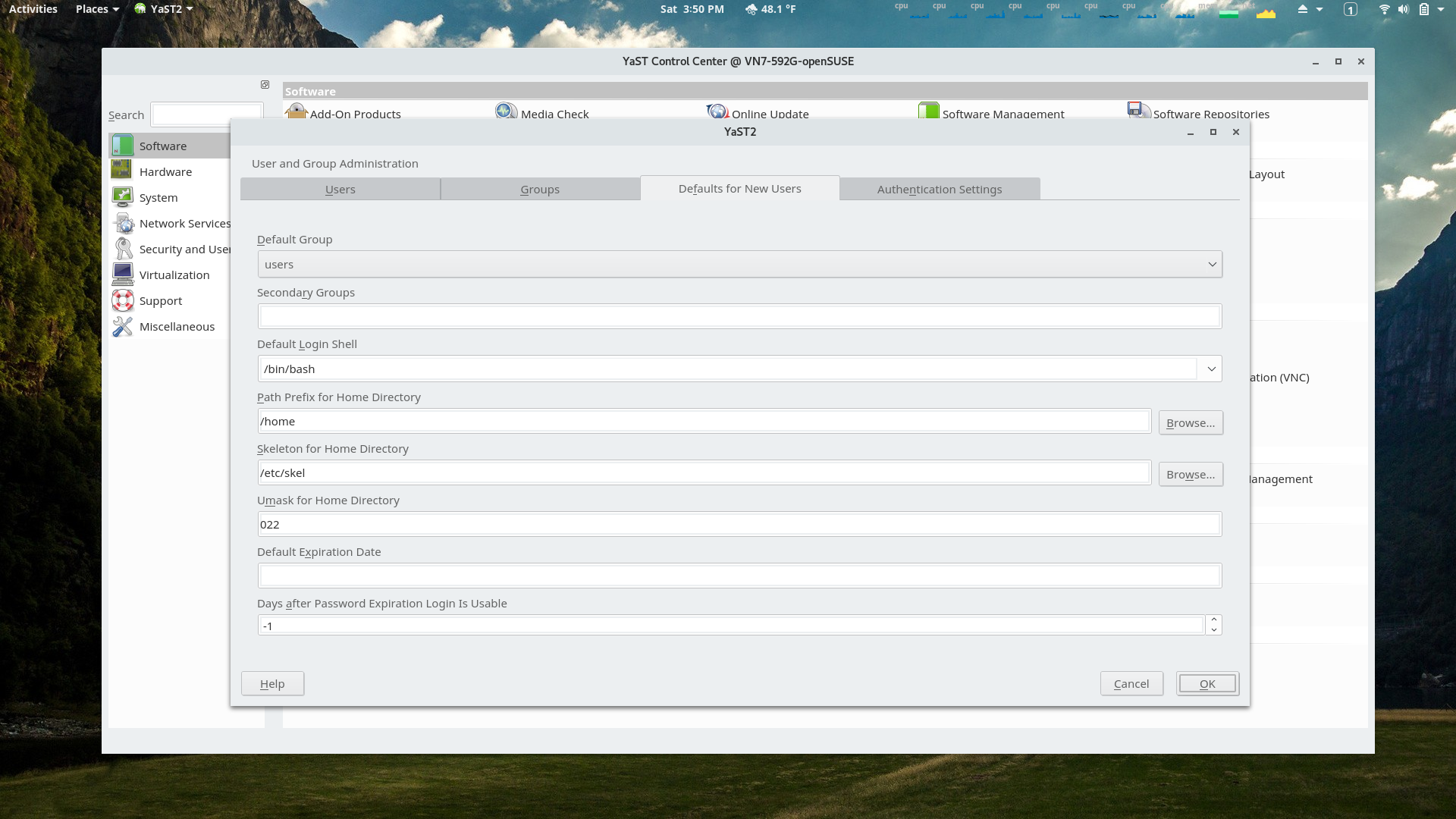
YaST Users and Groups Module
The Default Settings for New Users section of the module.
-
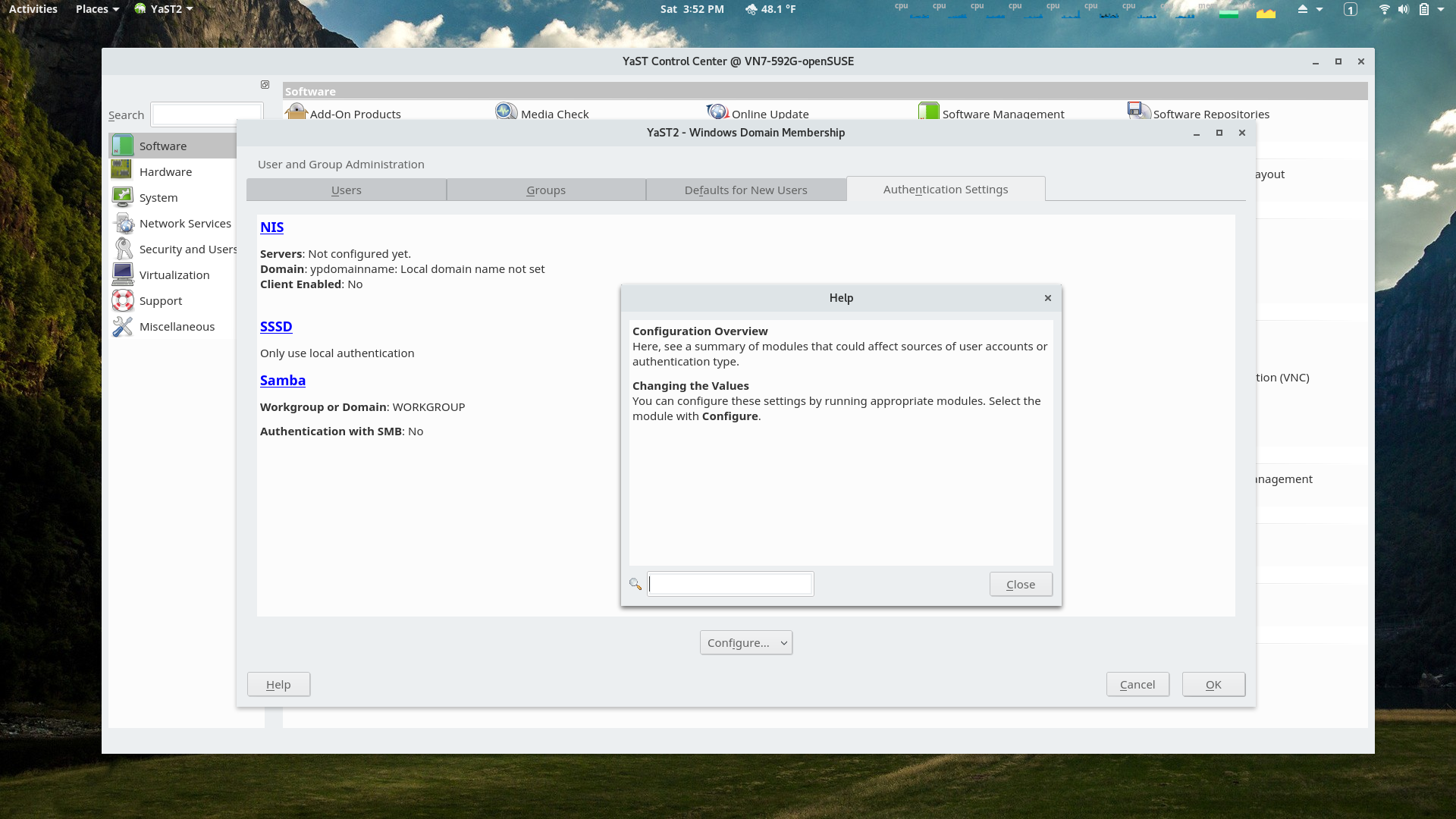
YaST Users and Groups Module
The Authentication Settings section of the module. Note the Help popup window which is available in all screens of all YaST modules.
-
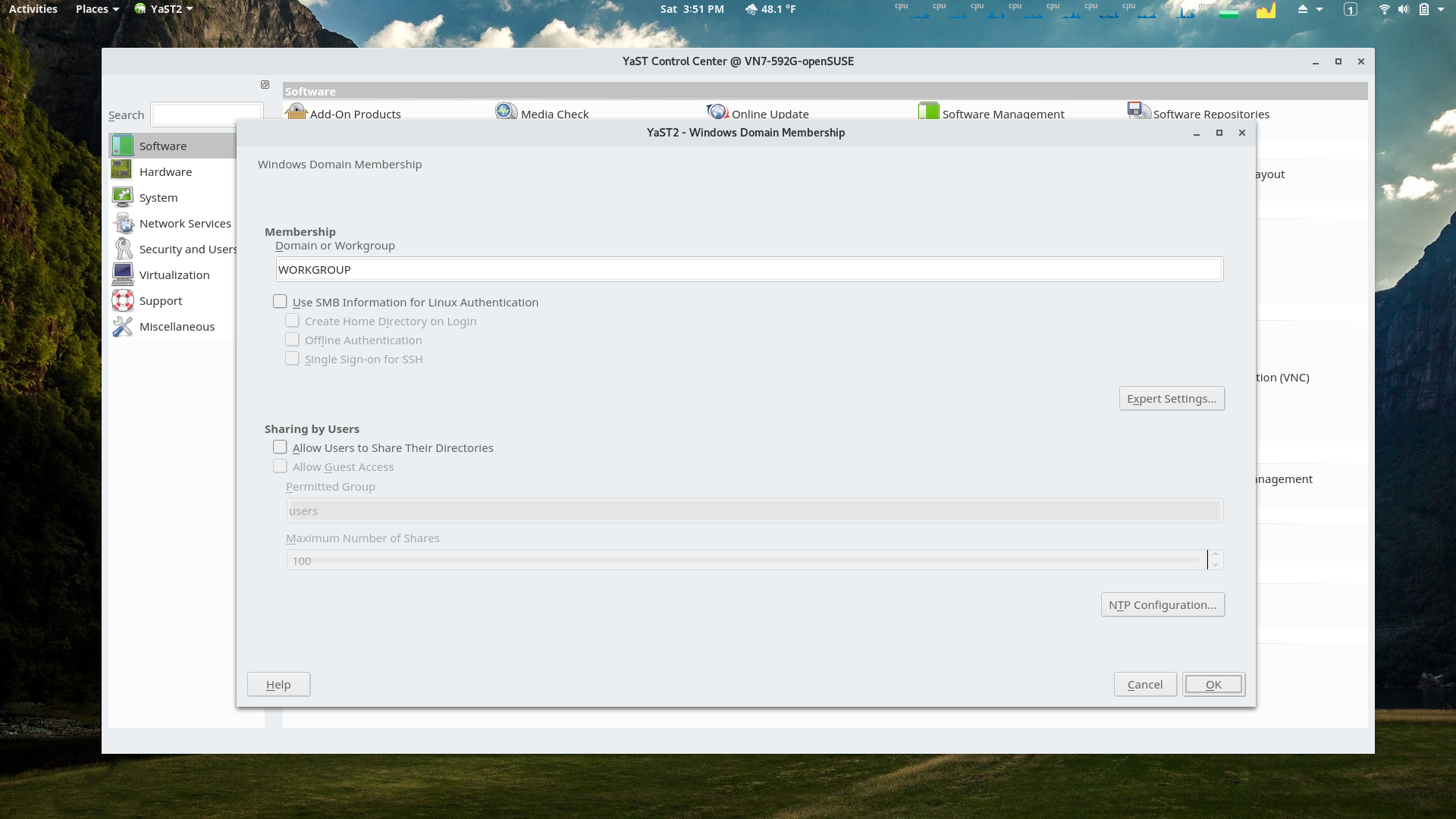
YaST Widows Domain Membership Module
Users on networks with Windows might find this helpful.
-
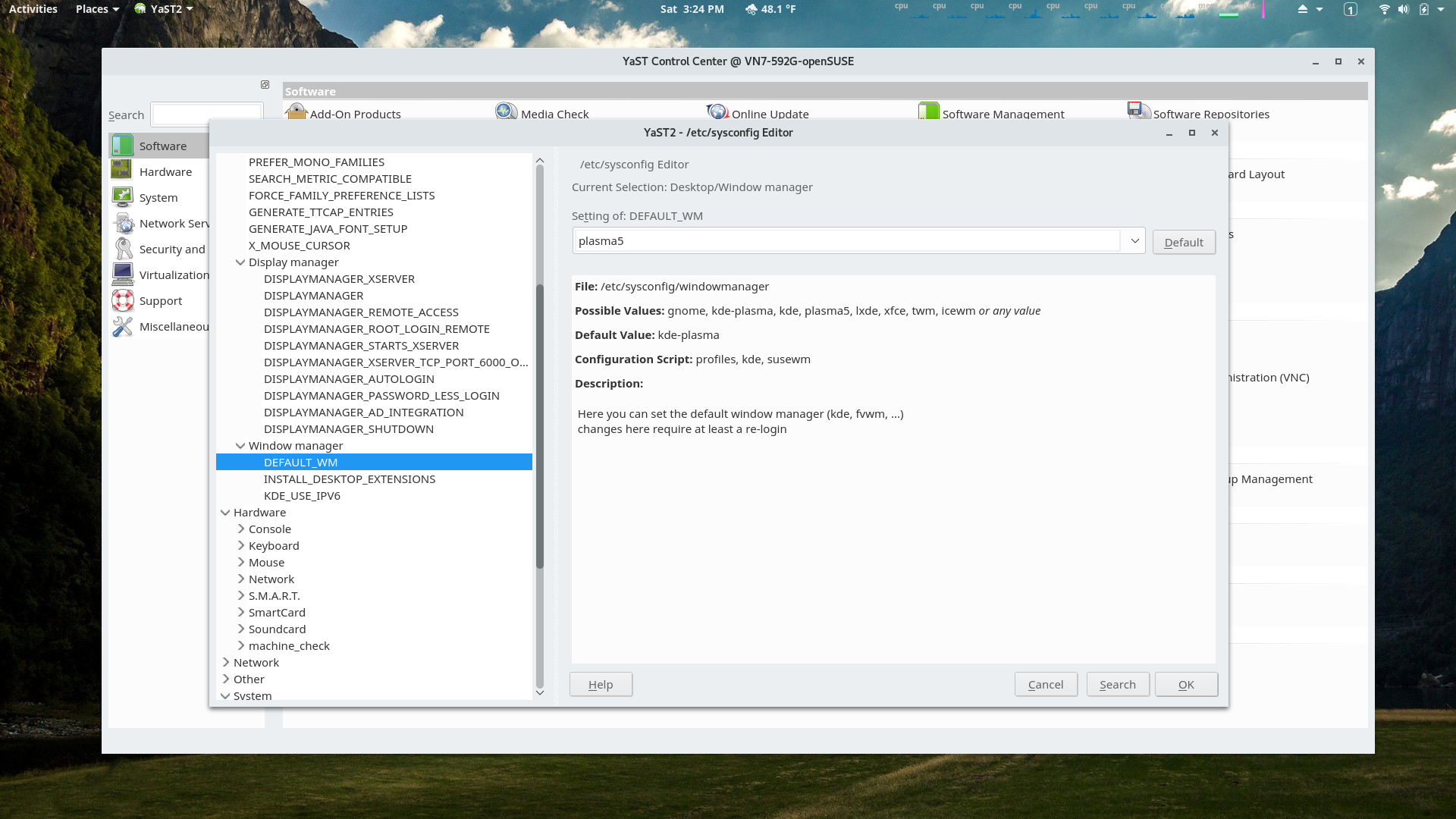
YaST /etc/sysconfig/ Editor Module
Configuring the default window manager using the /etc/sysconfig/ editor.
-
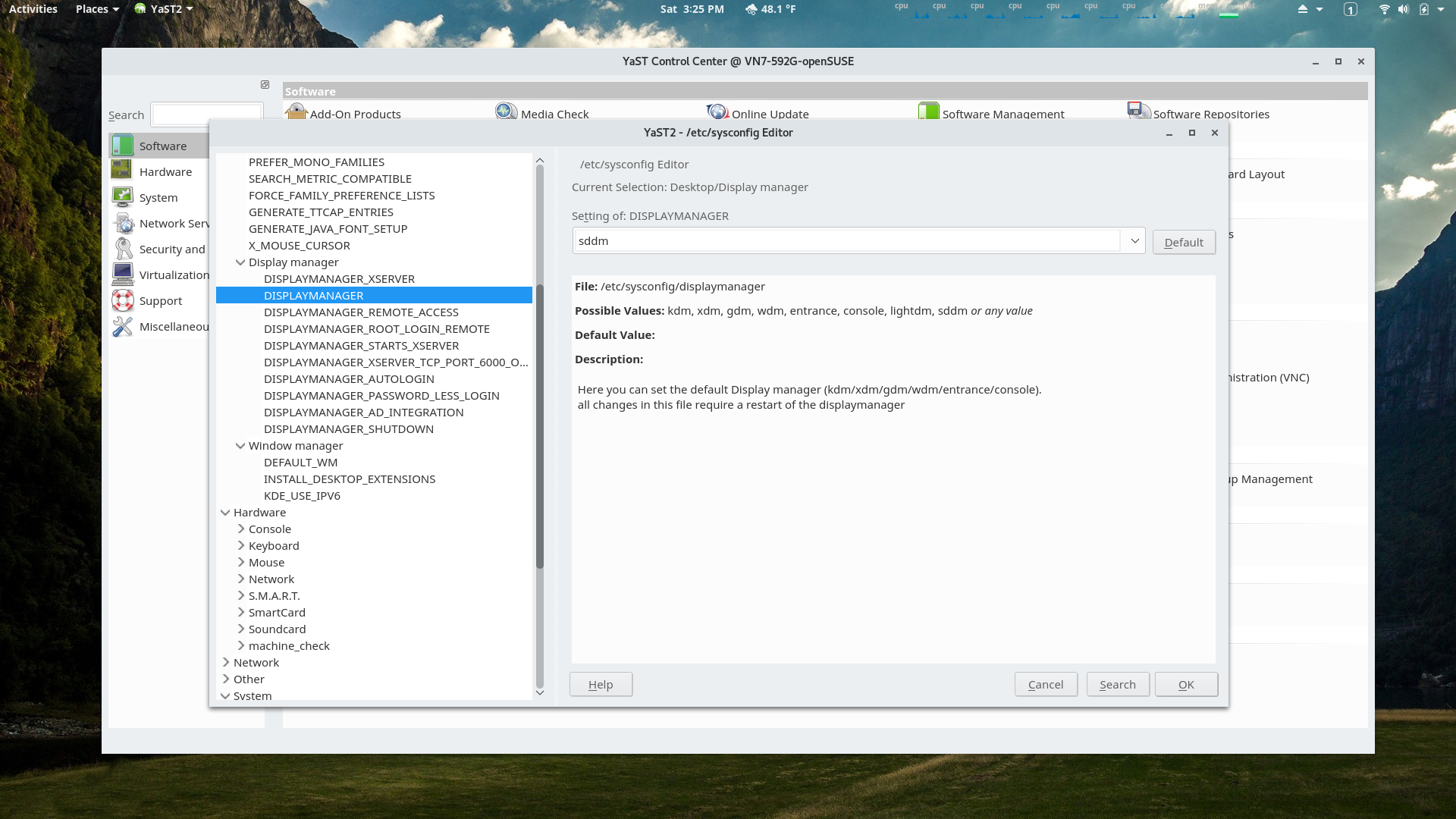
YaST /etc/sysconfig/ Editor Module
Setting the default display manager manager using the /etc/sysconfig/ editor.
-
YaST Systemd Journal Module
By default this module shows the entries since last boot.
-
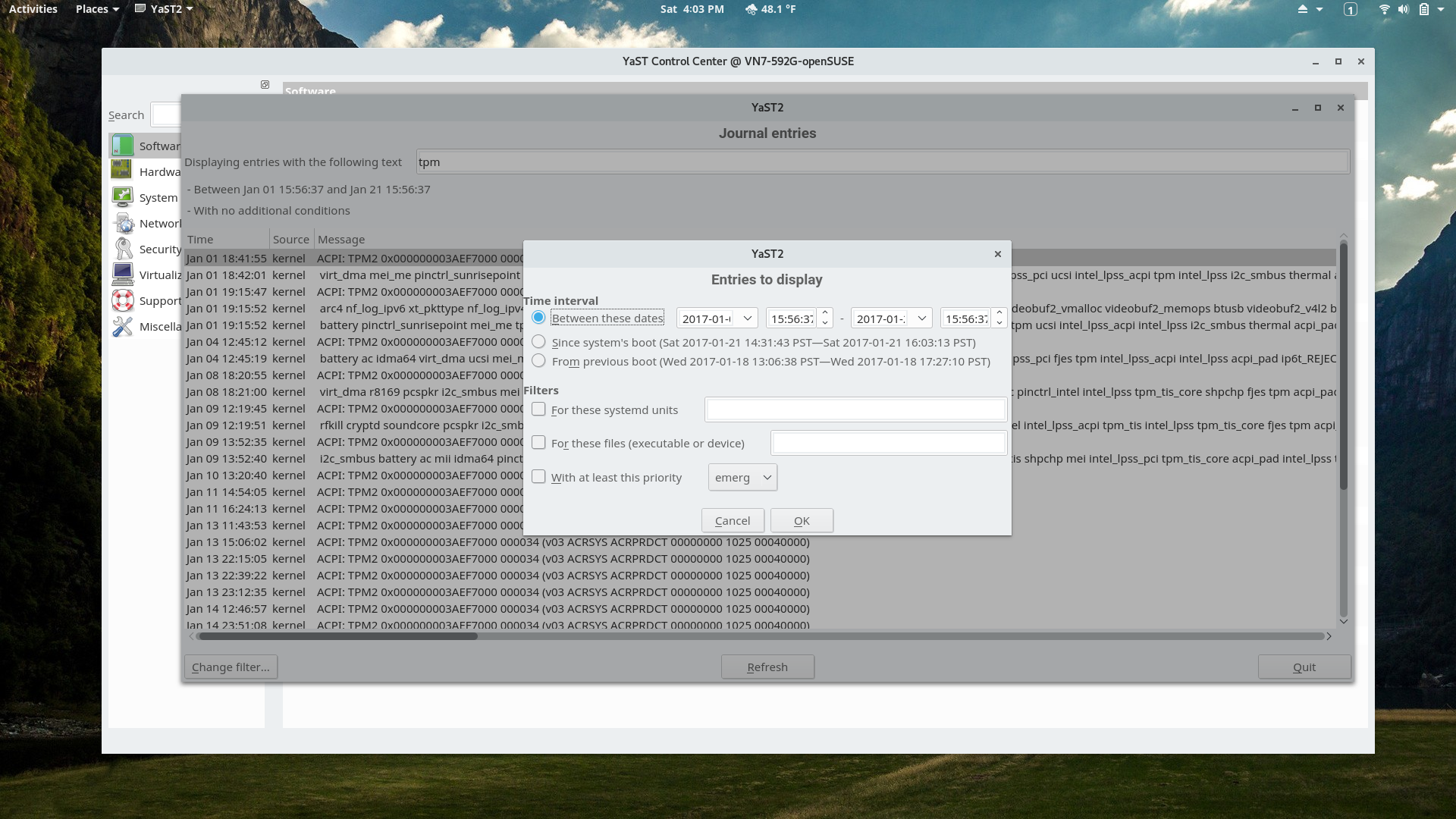
YaST Systemd Journal Module
Filtering options are available to select areas of the journal that are of interest. Considerably easier than using the journalctl command and its options in a terminal to find the source of a problem.
-
YaST Kernel Settings Module
The PCI ID Setup section of the module must be for advanced users.
-
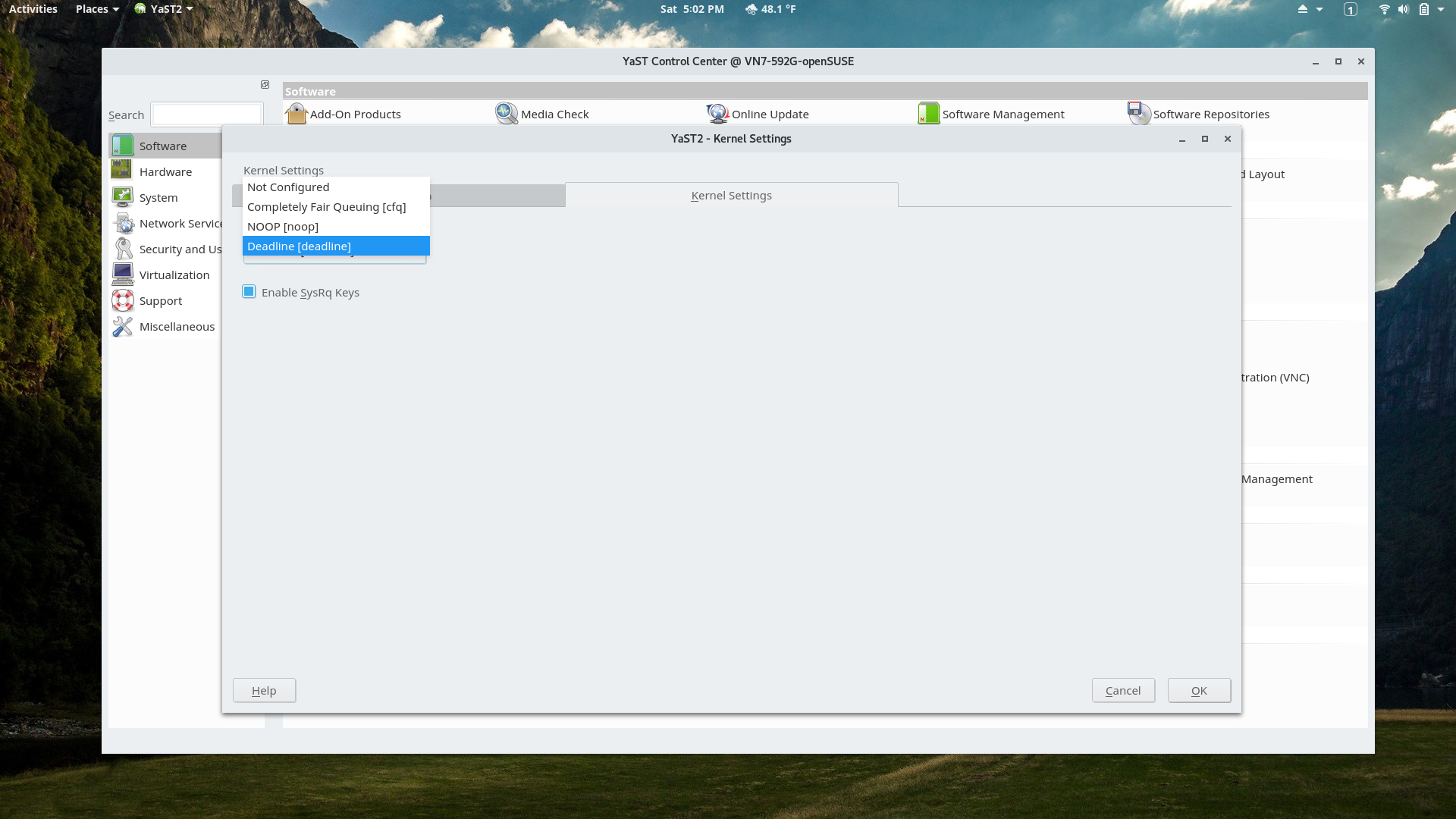
YaST Kernel Settings Module
This section of the module allows adjusting the IO scheduling. Unfortunately the module doesn't seem to be able to set scheduling per disk.
-
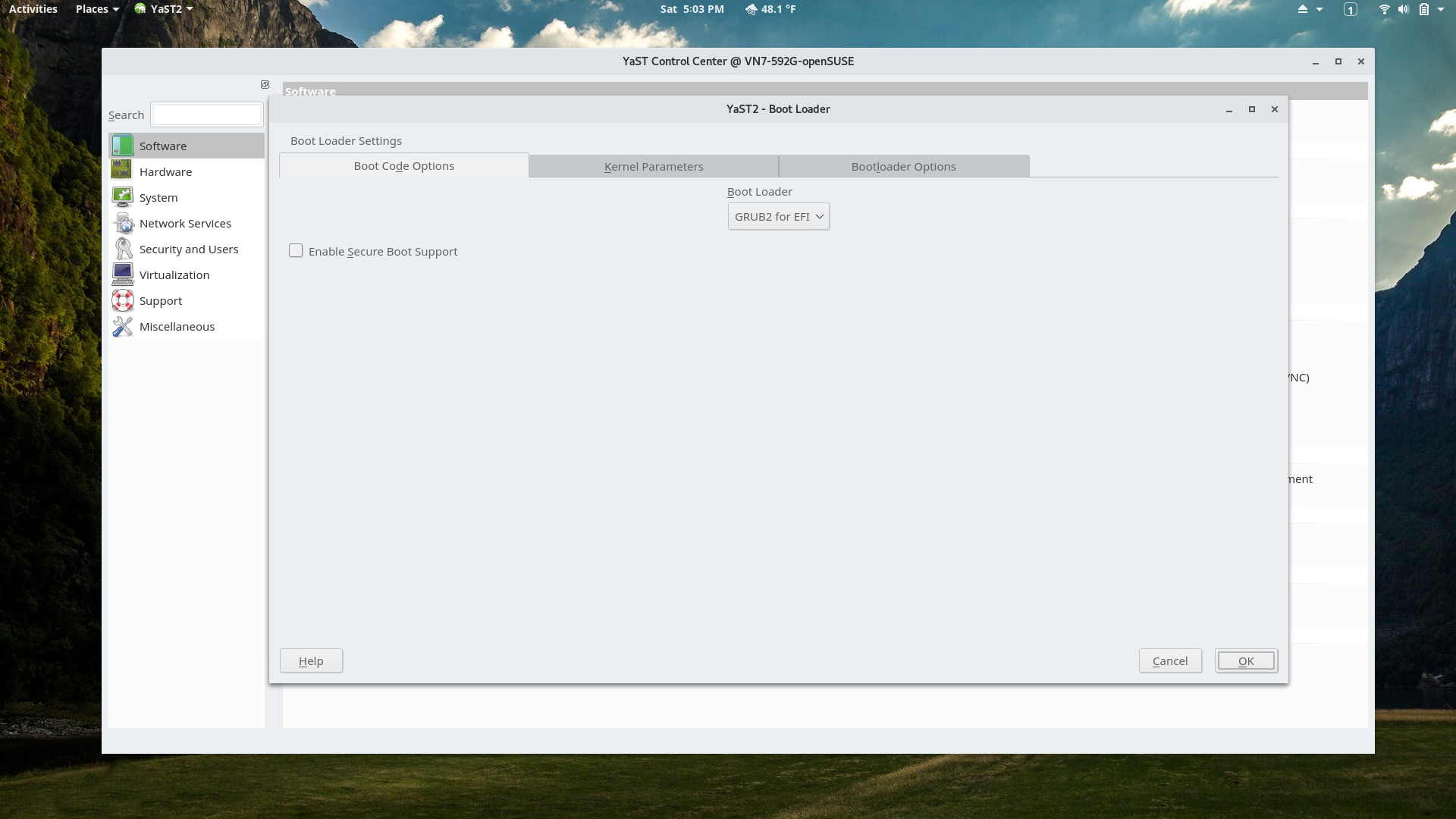
YaST Bootloader Settings Module
This module can install or reinstall the firmware bootloader and adjust settings.
-
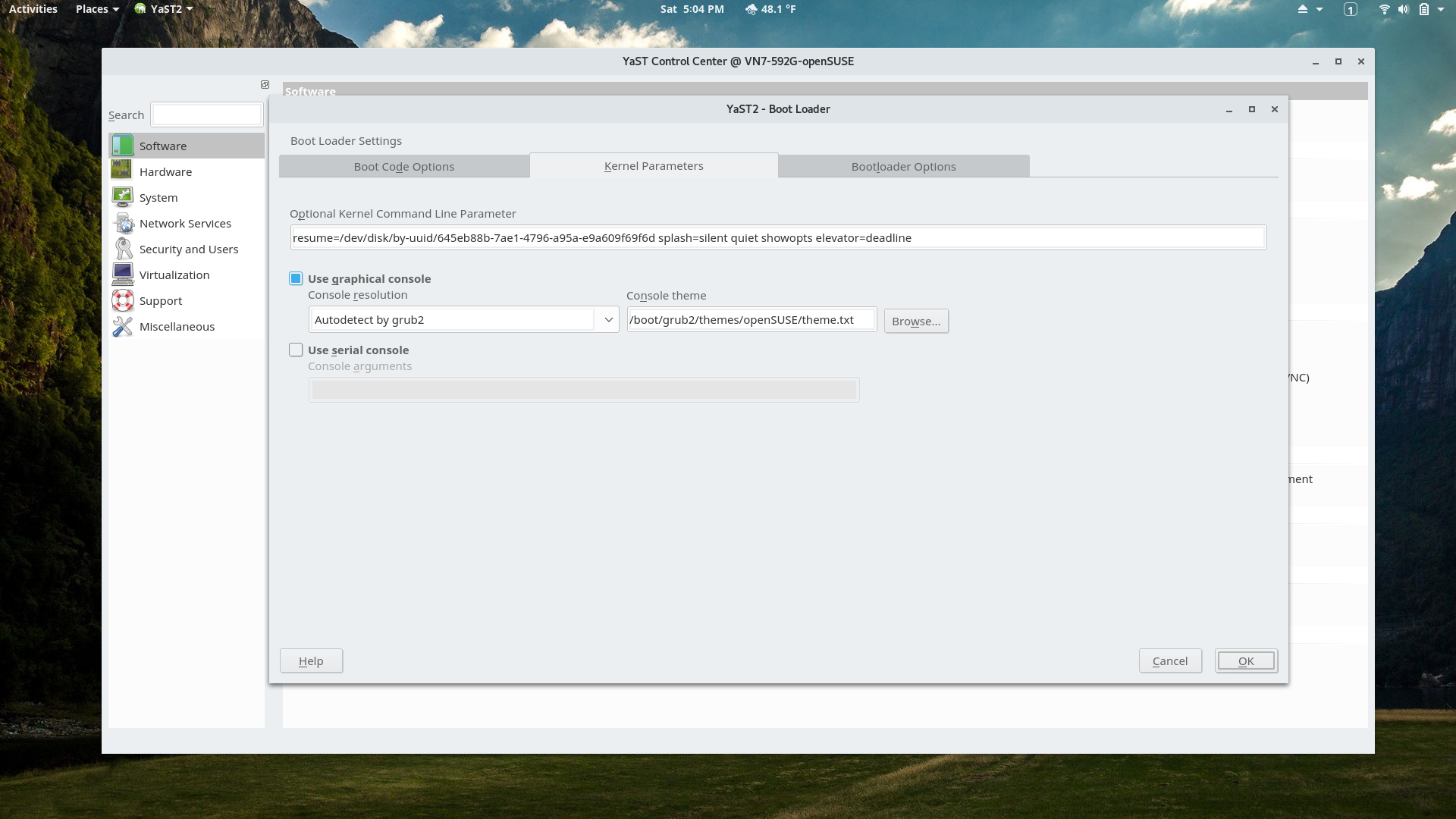
YaST Bootloader Settings Module
Kernel command line options can be set here.
-
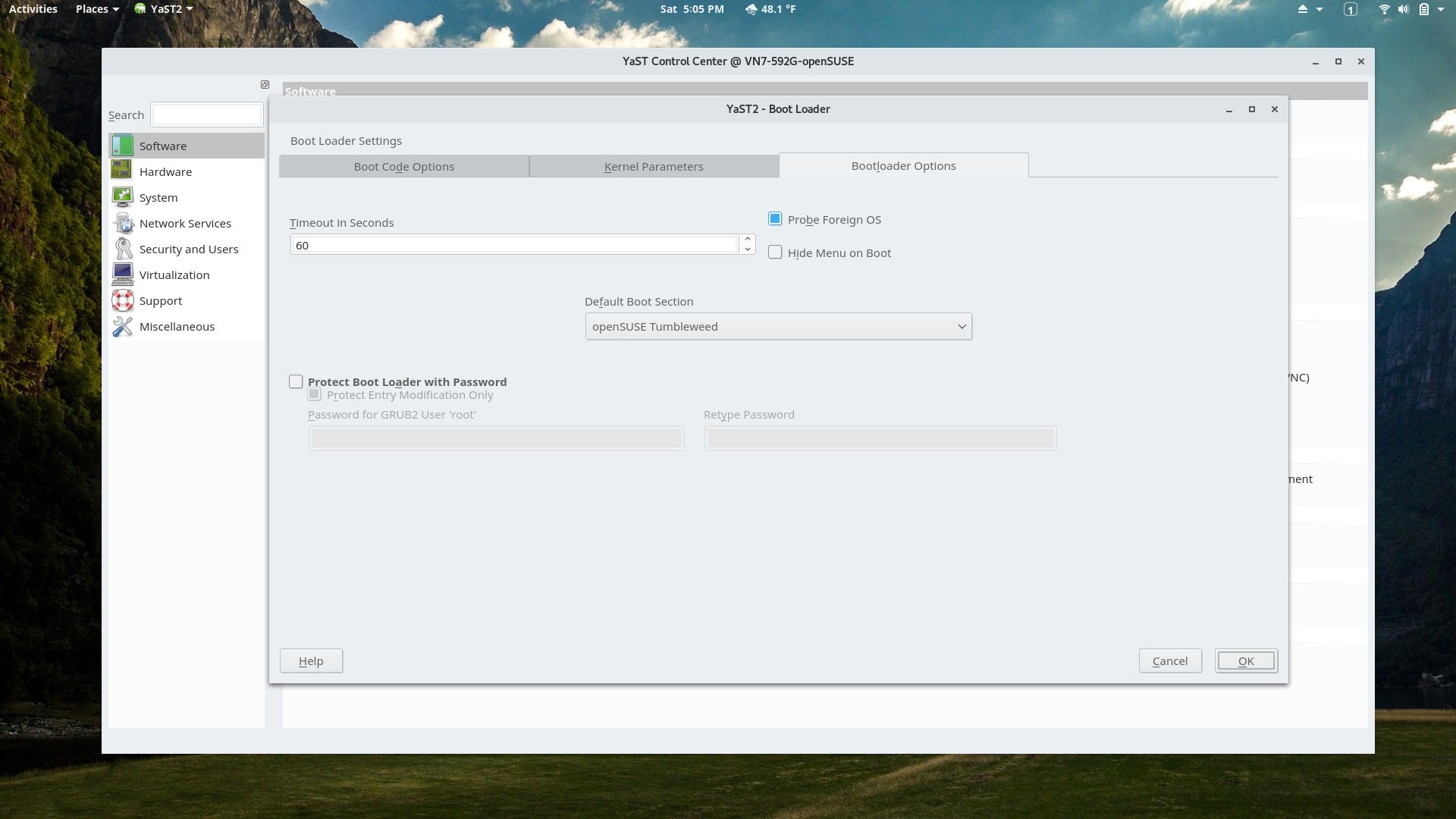
YaST Bootloader Settings Module
Some other GRUB options can be set here.
-
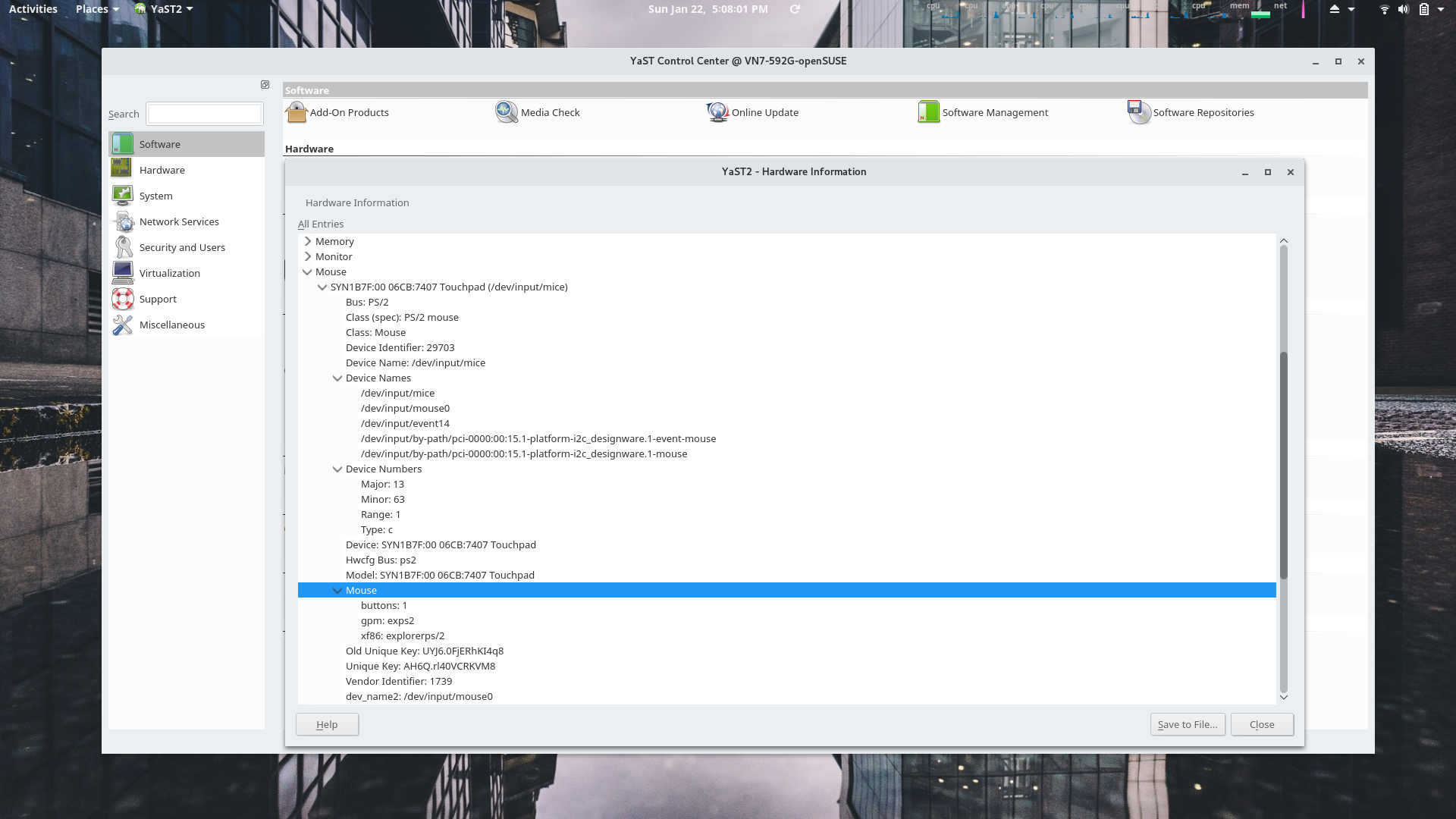
YaST Hardware Information Module
Another example of openSUSE's professional and polished feel provided by YaST is the Hardware Information module.
-
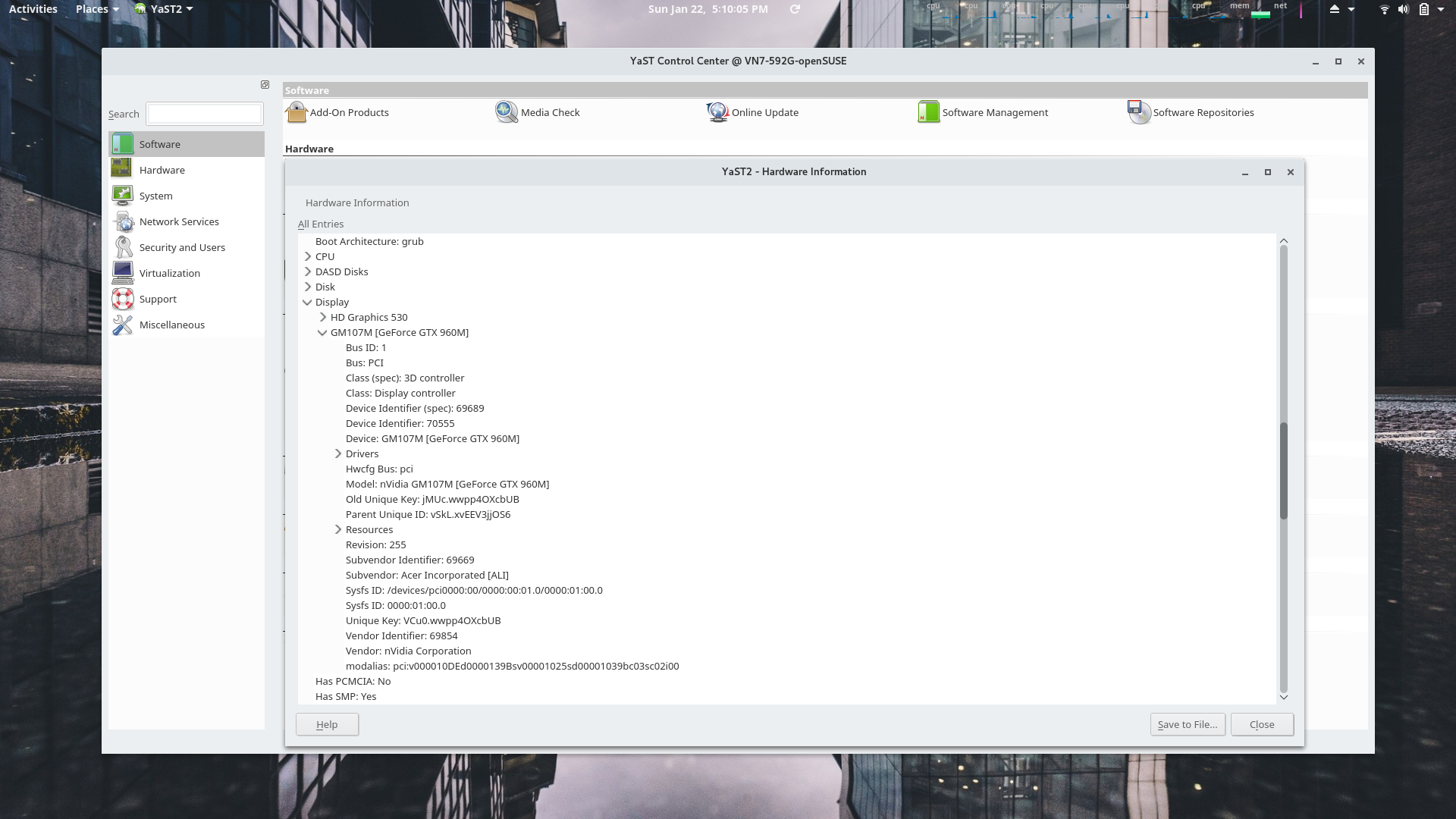
YaST Hardware Information Module
The display processors are displayed here with the Nvidia device expanded.
-
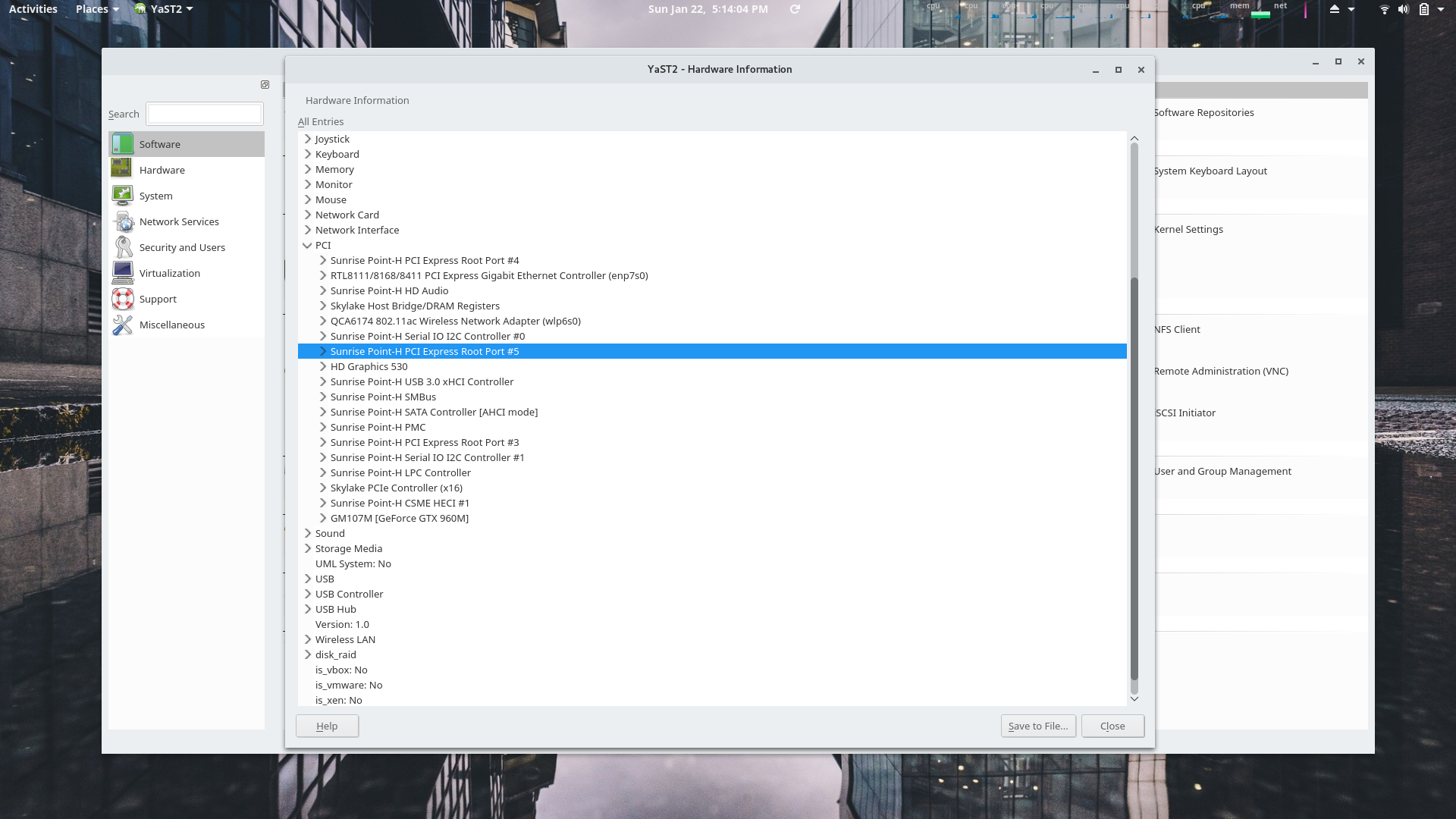
YaST Hardware Information Module
All PCI devices are shown here.
-
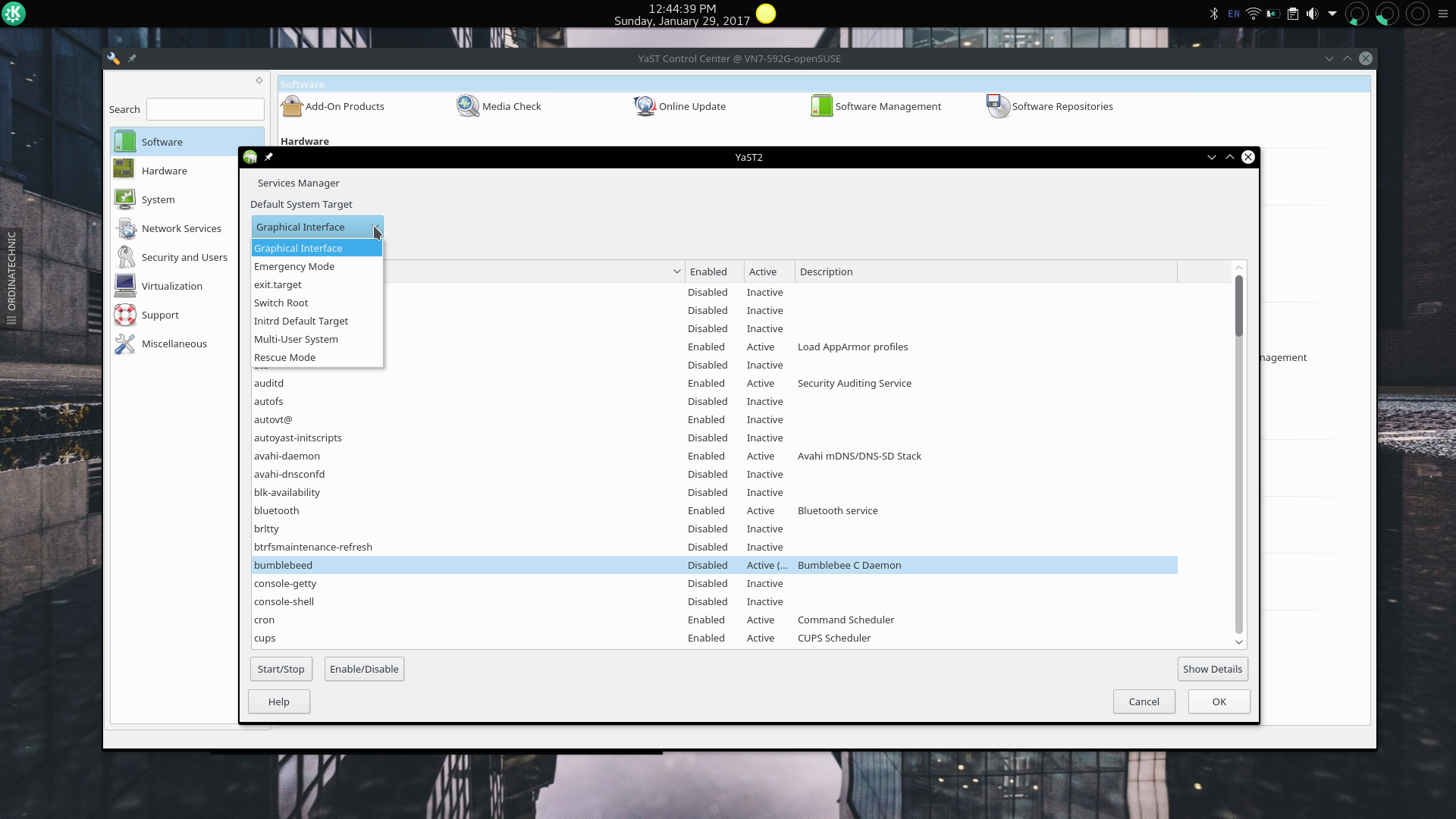
YaST Services Manager Module
The Services Manager module allows users to manage systemd services using the equivalent of running the systemctl program with the commands enable, disable, start, and stop.
-
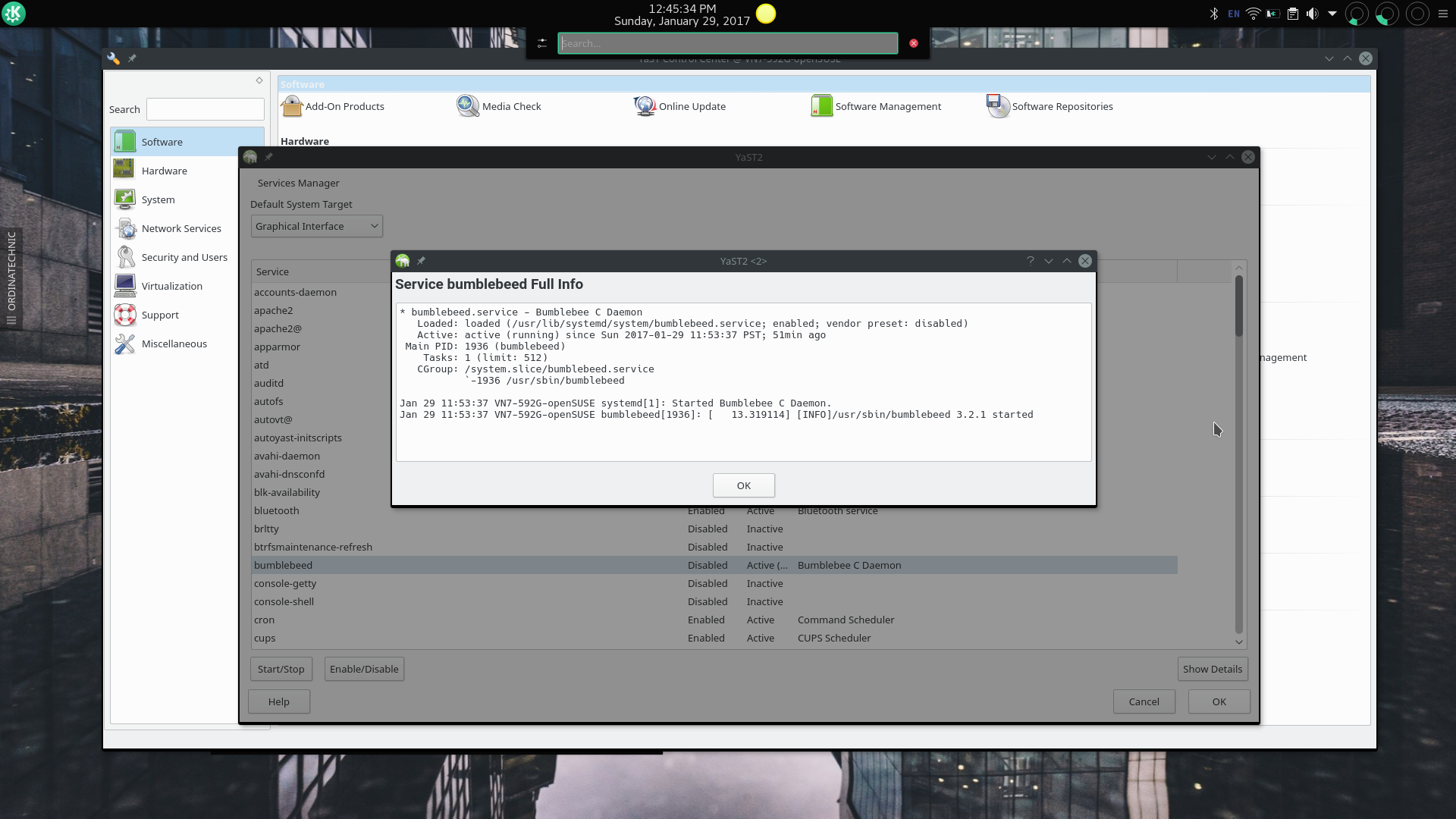
YaST Services Manager Module
The Services Manager module also allows users to display the detailed status of a service with the equivalent of systemctl status servicename.
Some of the YaST System Administration Modules.
YaST gives openSUSE users the option of administering the system with a comprehensive set of GUI tools or with the traditional approach of editing configuration files, and where required running programs that use these configuration files in a terminal. In my opinion this set of tools gives the impression that openSUSE has the same level of professional polish as UNIX workstations in their time.
The above set of slides show some of these YaST modules in use. All of these modules give the openSUSE user power and ease of use not available to users of other distributions, where configuration files must be edited manually and related programs that use these files run in a terminal. The availability of this suite of programs doesn't mean that the traditional methods are not available, giving openSUSE users flexibility that to use an all in one but modular GUI tool to administer the system or perform administration tasks from a terminal.
Anyone who has used another Linux distribution would agree there is nothing like it in any other distribution and would also realize all of these modules do nearly the same thing that can be done by editing a configuration file and/or running a program in a terminal. For example, the same thing that can be accomplished using the Bootloader Settings module can be done by
- installing/reinstalling the GRUB firmware bootloader in the ESP partition using
grub2-install --target=x86_64-efi
- editing /etc/default/grub to for example add kernel command line options
- running grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg in a terminal to update the configuration
Another example from the above slides is the
Systemd Journal module. One could run
journalctl --since="2017-01-01 15:56:37" --until="2017-01-21 15:56:37" | less
and then use the
less pattern matching command
&tpm to filter lines that contain "tpm" to produce the same information shown in slide 10, but it isn't as pretty as the output from the module.
The capability and robustness of YaST modules versus command line methods are not equivalent in all cases. Some modules may not be as robust as performing tasks in a terminal. The journalctl program, for example, has many more options in what data to display and how to display it compared to the equivalent YaST module. But the modules do simplify and improve the workflow of many system administration tasks. And again they are just an alternative to traditional methods.
The other significant element of openSUSE that demonstrates its excellent design is the command line package and repository management program (see screenshots on the next page) and its supporting infrastructure of configuration files and backend libraries (one of which, the dependency solver libzypp, was adopted by Fedora a few releases ago). The zypper program is well integrated into the relevant YaST modules. Unlike in Debian and Debian based distributions there is only one command line program that does everything (Debian has recently added a wrapper to the many apt-* commands to simplify its system) package management and repository management related. Its command line structure of commands, arguments, and options are intuitive, rational, and complete. See the reviews of openSUSE 13.2, openSUSE Leap 42.1, and the introduction to openSUSE repository management for examples. Even some more advanced tasks related to package management can be done directly from the zypper command line or the YaST modules such as repository prioritization without the complex apt pinning process of Debian. An openSUSE user may never have to look into the its Debian analog of /etc/apt/, /etc/zypp or edit any of these files in these directories. I've only had to do this once when adding the Opera's RPM repository instead of using zypper and this was due to Opera mishandling GPG keys.
The only file(s) that may need to be edited is one or both of the zypper related configuration files but only for general one time configuration of how zypper works. In my case I've only needed to edit the /etc/zypp/zypp.conf file to modify the number of and which past kernel versions to preserve during updates as a precaution against breaking the Nvidia for Bumblebee kernel module and to enable delta packages.
The core design of openSUSE is very good, but what about other less important aspects that some might care about such as theming, and usability and convenience adjustments. openSUSE doesn't do much in these areas. It usually has a very unique and original desktop background and Plymouth theme. Leap 42.1 used the striking gecko filament light bulb (this is used as the KDE startup background in this Tumbleweed installation snapshot), 13.2 used what seemed to be an abstraction of a gecko's scales as a desktop background which was also incorporated into the Plymouth theme. A little more work is done in the Plasma desktop with custom shell and window decoration themes, but these are usually just color adjustments to the stock theme provided by KDE. Other desktop environments are just stock besides the background.
Something that openSUSE does that I haven't seen in other distributions that specialize in KDE are special root profiles for the Konsole terminal and Dolphin File Manager. These profiles even have dedicated launchers. Strangely openSUSE does this only fore KDE Plasma and not Gnome, even though Gnome is also one the two prominent choices on the desktop selection screen; other desktop environment choices are only displayed after selecting other or selected from the software to be installed section later in the installation sequence.
As I mentioned in my openSUSE 13.2, openSUSE traditionally implements new Linux technologies and sometimes contributes to these projects. In that review I mentioned it was one of the first distributions to support UEFI and Secure Boot as well as systemd. Lately it has been the first to implement the btrfs filesystem, which allows the creation of system snapshots and allows booting into and rolling back to an existing snapshot.
The few times I used this feature, I found the ability to boot into a previous snapshot and rollback the system very impressive. In one instance while using openSUSE Tumbleweed I made a series of changes which broke some components of Plasma 5. I used the boot into an existing snapshot feature to boot into a snapshot which had a desktop environment installed which I had uninstalled after making the snapshot. What impressed me about this was the scale of the restoration, this wasn't just one or two files in a few directories, but from the aspect of what is visible to the user the entire system was different, and from the aspect of what is invisible every change to every file in the root file system was restored.
Although the Snapper/btrfs capabilities are useful, and work well as long as adequate hard drive space is allocated for the root file system, I chose not to use it in this installation of Tumbleweed for two reasons. First, the amount of disk space that should be allocated for btrfs is twice the disk space of what is necessary for the actual files, and in my case, there is not enough space on this Acer V15 Nitro's 128 GB primary SSD to preserve the preinstalled Windows 10 and install the root filesystems of the two Linux distributions I chose for permanent installation (data, home folders, and partitions for installation of Linux distros on temporary basis are on a second mechanical hard disk). Second, I don't know enough about whatever negative impacts there are to an SSD when using btrfs -- and how to mitigate these -- as opposed to the more typically used ext4 filesystem.
It seems that the aforementioned strengths openSUSE possesses is the result of its maturity -- it began in 1992 as SUSE -- and its basis as an enterprise operating system, with an interest in serving the needs of enterprise users and administrators. After SUSE was purchased by Novell and the openSUSE project was split from SUSE, openSUSE (and other distributions -- e.g. through the openSUSE Build Service) benefited greatly from Novell's support. During the time openSUSE was under the control of Novell the openSUSE infrastructure developed. Parts of this infrastructure are:
OBS (openSUSE Build Service)
-
The openSUSE Build Service is the public instance of the Open Build Service (OBS) used for development of the openSUSE distribution and to offer packages from same source for Fedora, Debian, Ubuntu, SUSE Linux Enterprise and other distributions..
-
The OBS provides optional repositories that users can add to get specialized, alternative, newer, or proprietary software. Some OBS repositories are for software packaged by upstream developers. openSUSE also allows and supports repositories created by ordinary openSUSE users.
Documentation Resources
- https://doc.opensuse.org
- This URL is the gateway to the formal openSUSE documentation -- an actual set of books -- available for consumption in many formats.
- https://www.suse.com/documentation
- This URL is the gateway to the formal SUSE documentation portal covering the SUSE Linux Enterprise Desktop as well as SUSE's other enterprise products.
- https://en.opensuse.org/Main_Page
-
The openSUSE wiki is not as comprehensive a reference as the Arch wiki, and in it is in need of some serious maintenance and reorganization, but it has some very useful articles, such as the one regarding Nvidia and Bumblebee.
SUSE Studio
- SUSE Studio allows users to create a completely custom image of various types including a live ISO image of a SUSE based distribution for many platforms including VMs.
One of the most helpful parts of this mature infrastructure for me has been the OBS which provided the Nvidia for Bumblebee proprietary driver for my current computer. This particular OBS repository allows openSUSE to adhere to its FOSS principles or legal compliance while giving users the option to benefit from the performance of the proprietary
Nvidia for Bumblebee drivers.
Unfortunately, over the years (I started using openSUSE while it was still SUSE in 2002 with a gap between 2005 through 2012) I've noticed that the attention that parts of this infrastructure were receiving has been inconsistent and were much better in the Novell days and steadily declined. The formal documentation that began as a set of complete books that came with the SuSe box set, and then available in many electronic formats were sometimes very outdated. With the release of Leap 42.2 though, it seems that everything has been updated. The wiki, however, remains very outdated, incomplete, and in need of reorganization. When I experienced the touchpad problem mentioned on the next page -- which was also an issue when I used Manjaro, I had to resort to the Arch wiki to learn about the issue and how to modify Xorg configuration files to remedy it.
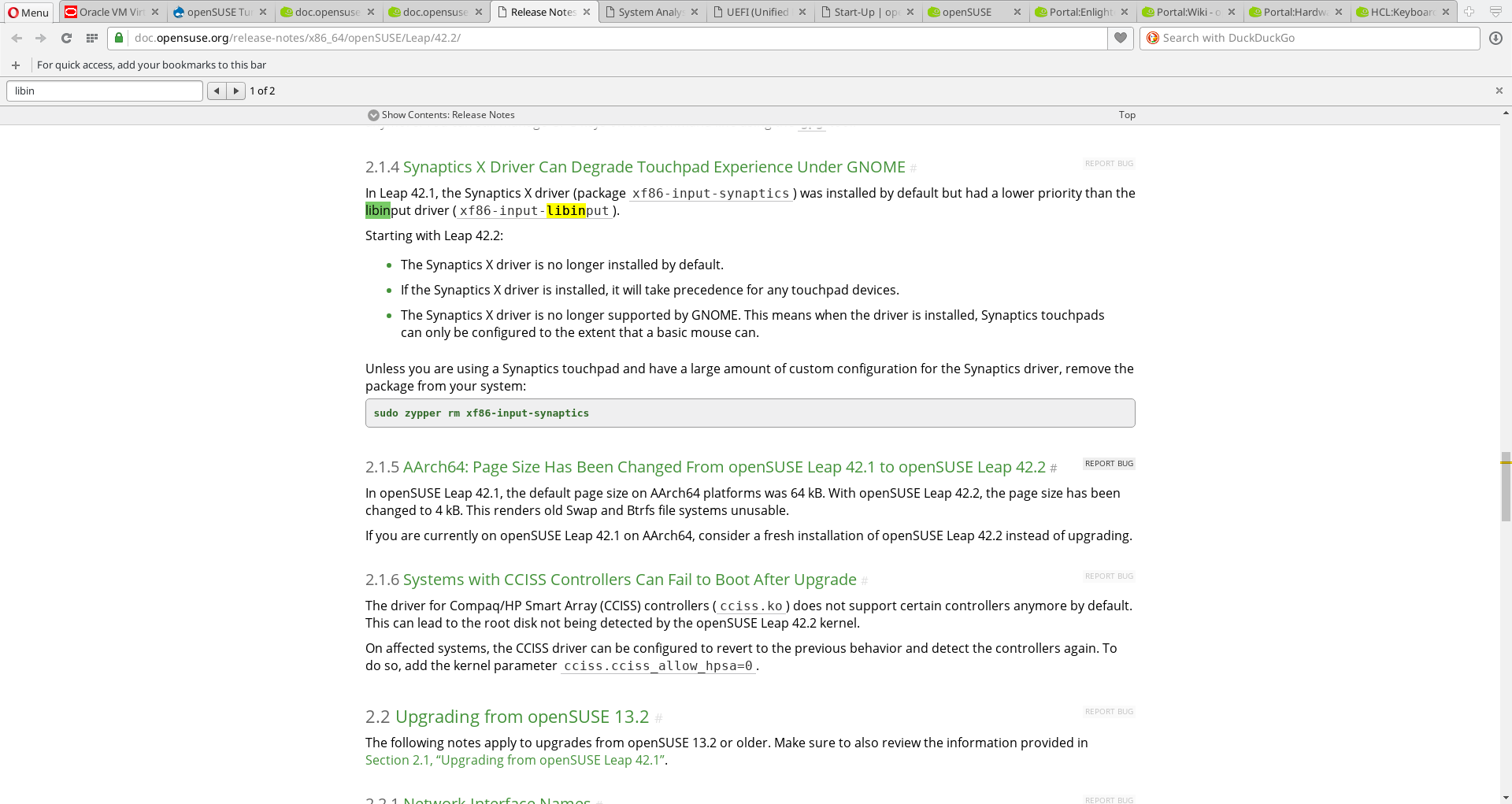
The Leap 42.2 Release Notes.
The release notes address a little of the issue but neither the openSUSE formal documentation or the openSUSE wiki provide comprehensive solutions to the issue as well as does the Arch wiki..
This is understandable as openSUSE can be considered the free version of a commercial product that provides resources to assist enterprise administrators with an online knowledge base that fills the same role as the wiki. But still, these.
Despite openSUSE's excellence in its fundamental design, power, flexibility, mature infrastructure, and adoption and contribution to cutting edge Linux features, it does suffer from some issues. Generally applicable to all releases and editions of openSUSE since 13.1 there have been many minor issues:
-
The installer usually has had some issues, although the current installation had no problems. My worst experience with the openSUSE installer was with the installation of 13.2. After the project decided to discontinue the live ISO (SUSE Studio is available for making a custom live ISO) the installer reliability improved for the regular release edition. Tumbleweed installation, however, continued to have issues. After successfully installing Tumbleweed in mid-2015 another installation in late-2015 was impossible because the installer switched to an ncurses type interface but not actually doing anything. I had to resort to installing Leap then doing a zypper dup to Tumbleweed. Fortunately, the current installation of Tumbleweed completed without any problems. (See the screenshots on the next page.)
-
The Plymouth boot animation is sometimes not properly configured sometimes displaying three dots and other times displaying three question marks on a blank background instead of the actual animation. This is usually resolved after additional the next boot or after an update.
-
Packaging sometimes has problems such that file conflicts occur during updates requiring the user to chose whether to keep the old or new version of a file. The conflicts are not with configuration files where zypper will save a new version of the configuration file with an rpm.new extension.
This installation of Tumbleweed in particular has seen its own specific problems.
-
One is a major annoyance in openSUSE's build of the KDE Plasma environment's Baloo file search and indexing system which I haven't seen with other distributions. At very short regular intervals Baloo causes the system to become completely unresponsive. The only solution that has worked for me has been to kill the associated processes
baloo_file and baloo_file_extractor immediately after logging into Plasma. This is unfortunate because the file indexing feature is used by the Plasma Search widget to produce search results impressively quickly. Manjaro's Plasma and Ubuntu's Plasma from the default 16.04 repositories or the Kubuntu backports PPA don't have this problem.
The implementation of Baloo in openSUSE Tumbleweed's Version of Plasma Is Very Problematic.
The frequent periodic system unresponsiveness caused by Baloo will annoy everyone who uses Tumbleweed's Plasma.
Another possible solution, which has been mentioned on some forum, may be to modify the ~/.config/baloofilerc file to change the setting first run=false after the system has been completely indexed. I made this modification to the config file which did not resolve the issue. The killing of the Baloo processes could of course be placed in a script and automatically executed using the KDE System Settings Module Startup and Shutdown.
-
I was also annoyed by touchpad performance with respect to palm detection when typing. The choices of which of the available Xorg input drivers to enable for the touchpad and the configuration of the chosen driver in /etc/X11/xorg.conf.d/ could have made a difference. This issue may have been exacerbated by my decision to select Plasma, GNOME, and Cinnamon desktop environements during installation. There is a little more on this issue on the next page.
-
The only other issue I've noticed in this specific installation Tumbleweed has been a problem with repository metadata during a major snapshot update that brought Plasma 5.9.0 to Tumbleweed, preventing zypper from successfully updating the package index. This type of issue is extremely unusual and has never happened in the almost two years that I've used Tumbleweed.
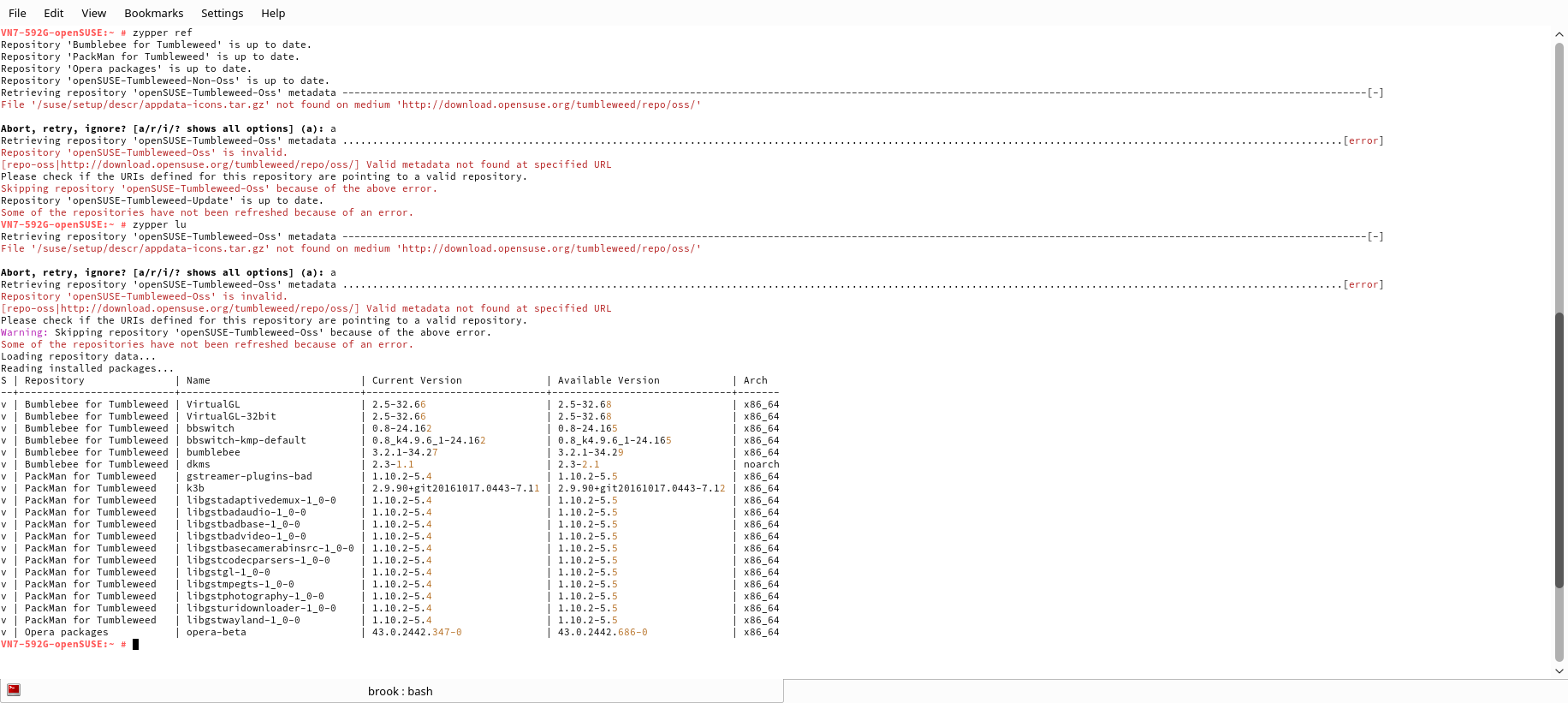
Konsole Terminal Showing the Output of a zypper Command Resulting in an Error.
This error caused by a problem with the repository metadate prevented an update to the installed Tumbleweed. This problem was resolved by openSUSE within two days the next time I attempted to update.
Most of these problems are minor annoyances with the exception of the Baloo problem which is more serious and needs the attention of openSUSE's contributes to KDE and openSUSE's packagers. Along with the other minor problems I've mentioned that apply to openSUSE in general, this is an indication that there needs to be additional quality control by the project. I've also noticed that there isn't a true separation between Tumbleweed and the regular releases, or there isn't a separation where there needs to be, as indicated by some non-user visible files still referring to 13.1. This lack of separation may be related to some of the little issues.
Despite these problems, I have been happy with using Tumbleweed for more serious activities since the middle of 2015, somewhat regularly on the retired Lenovo V570 and HP EliteBook 8450w, and almost exclusively on the Acer Nitro V15 Black Edition. It's always had current software without the breakage that sometimes occurs with Arch and its derivatives when depending on the AUR for software and the occasional unbearable inconvenience which comes with Arch. It doesn't have any of the problems of Sabayon, another rolling distribution that I found unusable long term. Only Manjaro comes close to Tumbleweed as being a permanent installation for daily use. However Manjaro, although it installs and configures the proprietary Nvidia hybrid graphics automatically at installation, did not properly configure the driver such that frame rates weren't improved by using the Nvidia processor. openSUSE however, after one simple process to install the optional packages from the OBS impressively impressively handled the installation, configuration, and subsequent updates of the proprietary Nvidia hybrid graphics with a proper configuration giving significantly improved frame rates when using the Nvidia driver.
openSUSE is a great distribution, and will remain as one of the two permanent distributions on the primary SSD. Hopefully the quality control that leads to the small issues I mentioned will be improved.
Necessary Fixes and Enhancements
PackMan Repositories
It is an absolute must to add PackMan repositories. The PackMan repositories for openSUSE provide some proprietary codecs as well as programs that require codecs with proprietary ones enabled, such as VLC. PackMan also provides both the PAPI and NPAPI versions of Adobe Flash as well as some other software that may not be available form openSUSE. The PackMan repsitory can be added using:
zypper ar -f -n "PackMan for Tumbleweed" http://ftp.fau.de/packman/suse/openSUSE_Tumbleweed/ PackMan_for_Tumbleweed
In the above, the repository URL is for the entire PackaMan repository which includes the
Essentials,
Extra,
Games, and
Multimedia repositories. If you want to choose just one of these repositories, maybe the most necessary repo being
Multimedia, append the name of the repository to the above URL as in:
zypper ar -f -n "PackMan for Tumbleweed" http://ftp.fau.de/packman/suse/openSUSE_Tumbleweed/Multimedia/ PackMan_for_Tumbleweed
Note that the
Extra,
Games, and
Multimedia repositories require the
Essentials repository, so that must be added first to use these repositories. Also note that you can choose the actual URL to specify for the repository by visiting
the PackMan mirrors page. Clicking any of the links on the mirror page will open a directory listing of the repository.
In addition to adding the PackMan repositories, they must be prioritized to prevent a change in package version during updates to those in the default openSUSE repositories. This is important for packages like vlc and vlc-codecs where the PackMan versions support proprietary codecs.
The Nvidia proprietary drivers and supporting packages such as dkms which is required for building the driver kernel modules should be installed from the relevant OBS repository.
Proprietary Nvidia Hybrid Graphics
openSUSE configures the Open Source Nouveau driver by default even for a system with hybrid graphics. I would enable the proprietary Nvidia driver for Bumblebee as described here.
What Works and What Doesn't
Hardware
Every piece of hardware worked well with openSUSE Tumbleweed including all keyboard function keys, backlight control -- without any kernel parameters, WiFi, Bluetooth, and as previously mentioned the hybrid graphics with proprietary Nvidia drivers (for use with Bumblebee). At first I thought Bluetooth wasn't working because the default installation allowed pairing and connecting to my LG Tone PLatinum (HBS-1100) but could not output any audio to it. This was actually due to KDE Plasma settings. After playing with the audio settings, accessible through the Multimedia Settings of KDE System Settings, called Configure Desktop in openSUSE's implementation of the Plasma Desktop, I was able to output the audio to the headset. The configuration in openSUSE actually works so well the pairing created in KDE continued to work automatically in GNOME.
The only hardware related issue that I have is not really a problem but configuration choices openSUSE made with the respect to input device related Xorg drivers. The issue is that in Plasma the touchpad is not disabled when the setting to disable the touchpad when typing is activated.
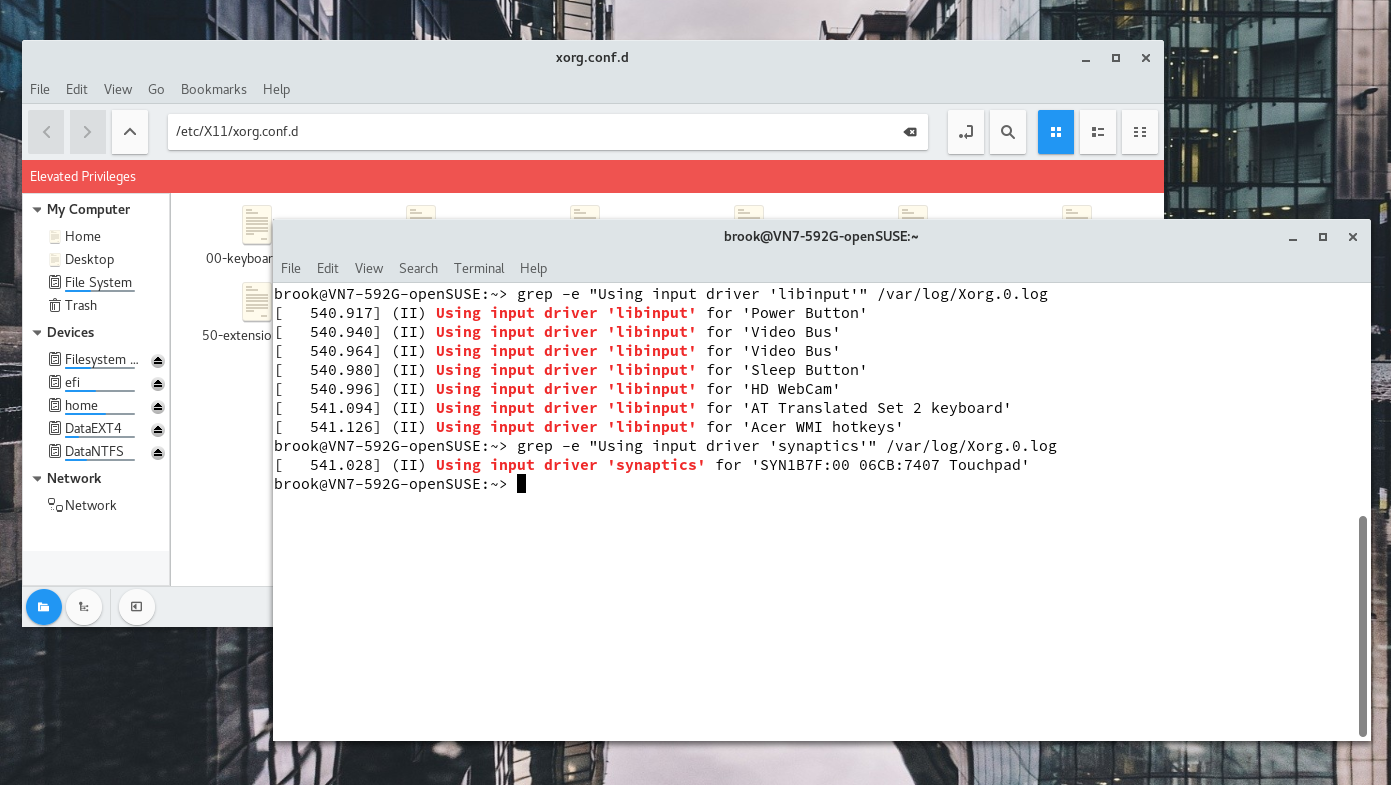
Devices Using libinput and synaptics Drivers
All relevant devices are using libinput except the touchpad which is using synaptics.
This problem can probably either by using the
libinput driver for the touchpad as well as the other devices, or modifying the configuration of the
synaptics driver. The Arch wiki discusses the issues on its
synaptics and
libinput pages.
Multimedia Codecs
Another lingering problem I've experienced that has nothing to do with openSUSE -- and in fact may be entirely due to the ad blocking and privacy extensions that I use in Opera or sites blocking Flash -- has been an intermittent problem with Flash in Opera browsers. In the past the PackMan repositories provided the Pepper Flash Plugin extracted from the Chrome browser. More recently, after it became more difficult or impossible to extract the Pepper Flash Plugin from Google Chrome it was possible to install Google Chrome just to let Opera have access to its included Pepper Flash Plugin. Recent editions of Google Chrome however install the Pepper Flash Plugin in a subdirectory of the user folder (at ~/.config/google-chrome/PepperFlash/24.0.0.186/libpepflashplayer.so) instead of the traditional subdirectory of the root filesystem (at /usr/lib64/chromium/PepperFlash/libpepflashplayer.so where Opera can find it.
Since Adobe resumed support of Flash for Linux recently, the PackMan repositories have been providing two versions of Flash one version for NPAPI browsers such as Firefox and another version for PAPPI browsers such as Chrome and other Chromium based browsers. The NPAPI version works without any problems that I have noticed in Firefox, but the PAPPI version in Opera doesn't work on some sites -- again this may be due to extensions not working well in Opera or measures taken by sites to force the viewing of ads or pop-ups, as I've lately seen similar behavior in Chrome.